Fig. 5.
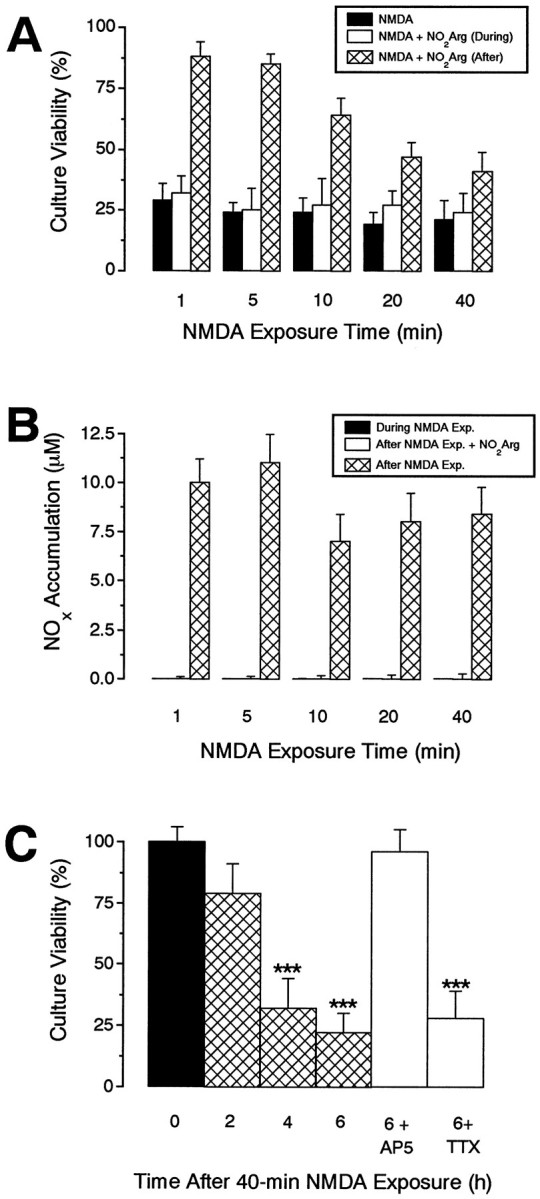
NMDA-triggered neurodegeneration can be independent of NOS and TTX-sensitive sodium channels. A,B, Effects of prolonged NMDA exposure on culture viability and NOx accumulation. Cultures were exposed to NMDA (100 μm) for various periods in the presence or absence of nitroarginine (NO2Arg, 100 μm) and were then allowed to recover for 24 hr in the presence or absence of nitroarginine (100 μm) before culture viability (A) and NOx accumulation (B) were assessed. Note that nitroarginine becomes progressively less effective in providing neuroprotection with increasing NMDA exposure times (A), whereas it efficiently inhibits NOx accumulation irrespectively (B).C, Kinetics and pharmacology of NO-independent NMDA-triggered neurodegeneration. Cultures were exposed to NMDA (100 μm, 40 min), and culture viability was assessed at 0, 2, 4, and 6 hr later. Other cultures were exposed to NMDA (100 μm, 40 min) and recovered for 6 hr in culture medium containing AP5 (100 μm) or TTX (1 μm). Note that the kinetics of neurodegeneration is faster than is observed after a brief (5 min) NMDA exposure (Fig. 2A) and that it is insensitive to TTX. All values are mean ± SEM of two to three separate experiments (with at least 3 culture wells per treatment per experiment). *p < 0.001 from control groups (time = 0 hr).
