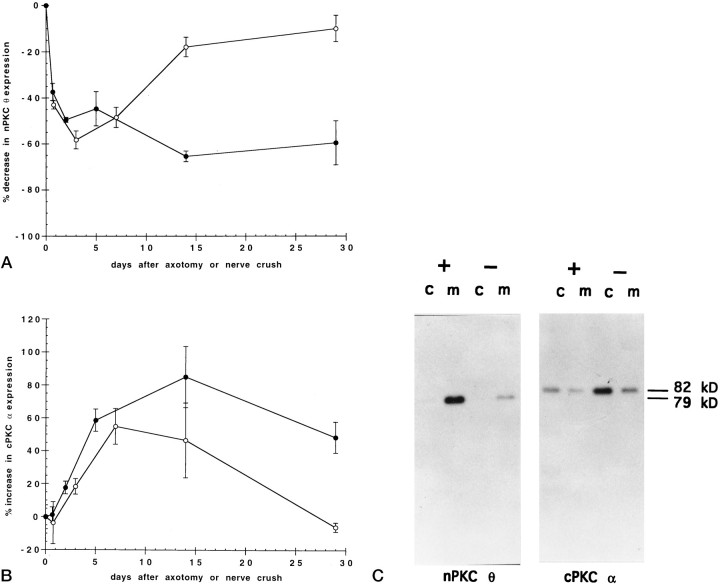
Fig. 1.
Time course of nerve crush or axotomy on PKC expression in skeletal muscle. The phrenic nerve to rat diaphragm muscle was unilaterally severed (axotomy) (•) or crushed (○), and the rats were allowed to recover for the indicated times. Diaphragms were then removed, homogenized, and separated into cytosolic and membrane protein fractions by ultracentrifugation. Cytosolic (c) and membrane (m) proteins (50 μg) from both denervated and control hemidiaphragms from each rat were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Immunoblots were probed with antiserum specific to nPKC θ (A) or antibody specific to cPKC α (B) followed by a secondary antibody and 125I-labeled protein A. The blots were exposed for autoradiography, and radioactivity was quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis using ImageQuant software. Data are expressed as percent decrease in nPKC θ (A) or increase in cPKC α (B) expression in cytosolic plus membrane fractions of experimental compared with control hemidiaphragms of the same rat. Error bars represent SEM. For each point, n = 3 or 4 rats. C shows a representative autoradiogram of an immunoblot from 14 d axotomized (−) and control (+) hemidiaphragms.