Figure 1.
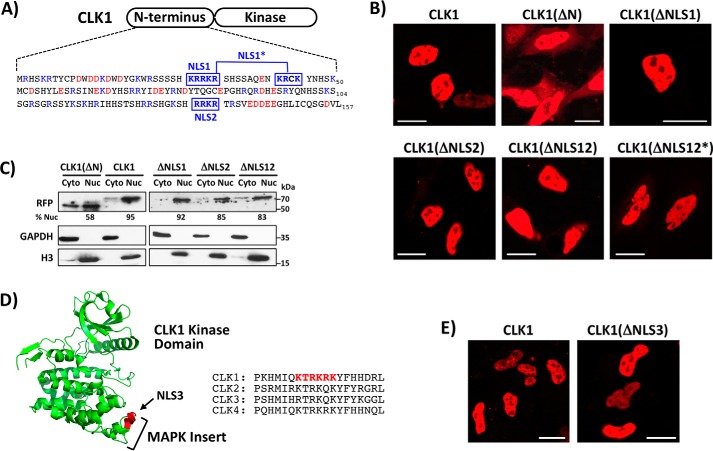
CLK1 N-terminus lacks a short, positively charged NLS. A, N-terminal sequence of CLK1 and several, short potential NLSs identified by cNLS Mapper. NLS1 and NLS2 represent monopartite NLSs, whereas NLS1* represents a bipartite NLS. B, live-cell confocal imaging of HeLa cells expressing WT CLK1 with a C-terminal RFP tag along with mutant forms where the putative NLS residues are mutated to glycine. NLS regions are defined in A. ΔNLS12* represents glycine mutations in both NLS1* and NLS2. C, fractionation of HeLa cells expressing WT CLK1-RFP and several mutants. ImageJ was used to quantitate the amount of RFP-tagged proteins in the nucleus (% Nuc). D, potential NLS in the MAP kinase insert of the CLK1 kinase domain. Regional sequences of the potential NLS are compared with those in other human CLKs. E, live-cell confocal imaging of HeLa cells expressing WT CLK1-RFP and a form where Lys/Arg in NLS3 is mutated to alanine. Scale bars, 20 μm.