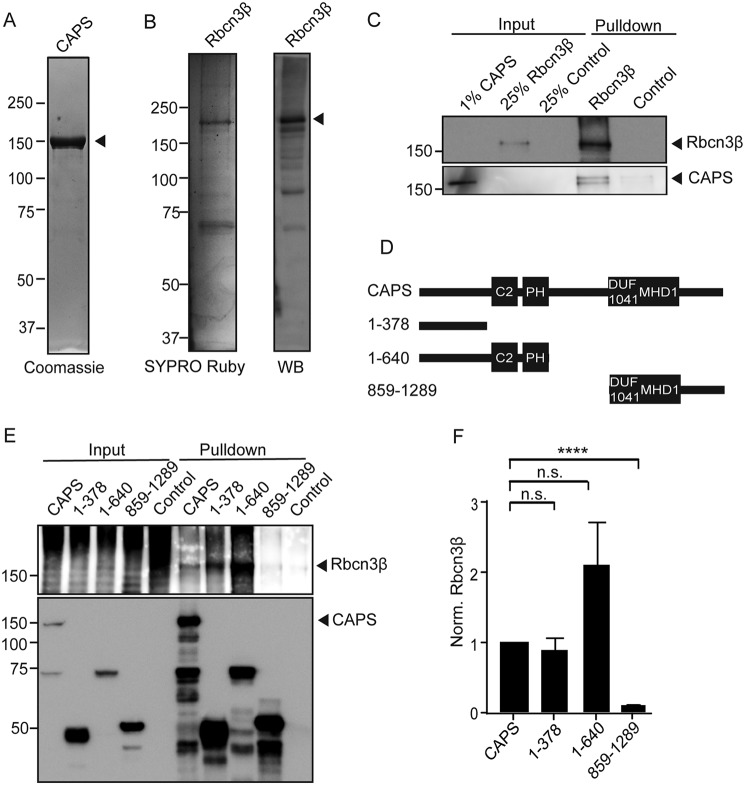
Figure 4.
CAPS1 directly binds to Rbcn3β. A, Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing CAPS1-TwinStrep purification from HEK cells. The arrow points to CAPS1-TwinStrep. B, SYPRO Ruby–stained SDS-PAGE showing Rbcn3β-GFP purification from HEK cells (left) and a Western blot (WB) of purified Rbcn3β-GFP (right) with Rbcn3β antibodies to show that several degradation bands were present. The arrow points to full-length Rbcn3β-GFP. C, Western blot showing binding of purified CAPS1-TwinStrep interacting with purified Rbcn3β-GFP. A representative of four similar studies is shown. D, scheme depicting CAPS1 domains and the HA-tagged CAPS1 fragments used for HA immunoprecipitations. C2, PH, DUF1041, and MHD domains are depicted. E, representative Western blot depicting pulldown of CAPS1-HA fragments and coimmunoprecipitation of Rbcn3β. 5% of the input fraction was loaded. In the concentrated input lanes for Rbcn3β, aggregation and degradation were reproducibly observed. F, relative Rbcn3β bound to CAPS1 fragments normalized to the amount of CAPS1 pulled down. Values shown represent means ± S.E. (n = 3). ****, p < 0.001; n.s., nonsignificant.