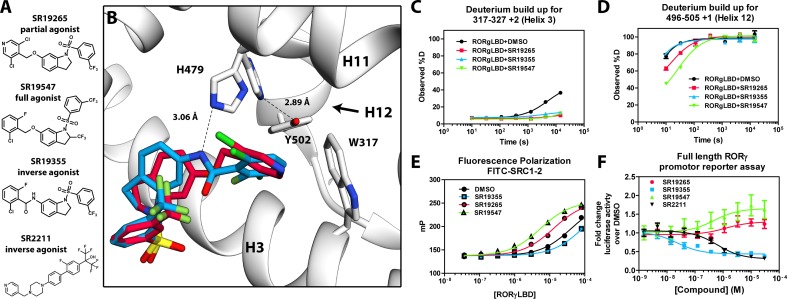
Figure 2. Mechanism of action for select N-arylsulfindoline RORγ modulators.
(A) Representative structures of four modulators and their pharmacology. (B) Co-crystal structure solutions of SR19265 and SR19355 reveal mechanism of action. A peptide bond on SR19355 acts as a hydrogen bond donor for H479 and disrupts H479 and Y502 hydrogen bond. (C, D) Differential HDX-MS was employed to evaluate ligand dependent structural perturbations in solution. Representative deuterium build-up plots showing Helix 3 (C, H3) and Helix 12 (D, H12) dynamics. (E) fluorescence polarization results showing gradient of affinity for coactivator peptide depending on compound. (F) RORγ modulators were tested in a cell-based promotor reporter assay. Vectors encoding full length RORγ and a 5xRORE-Luciferase promotor reporter were transiently transfected into HEK293T cells. These cells were seeded into a 384 well plate and tested for dose-dependent responses to compounds.