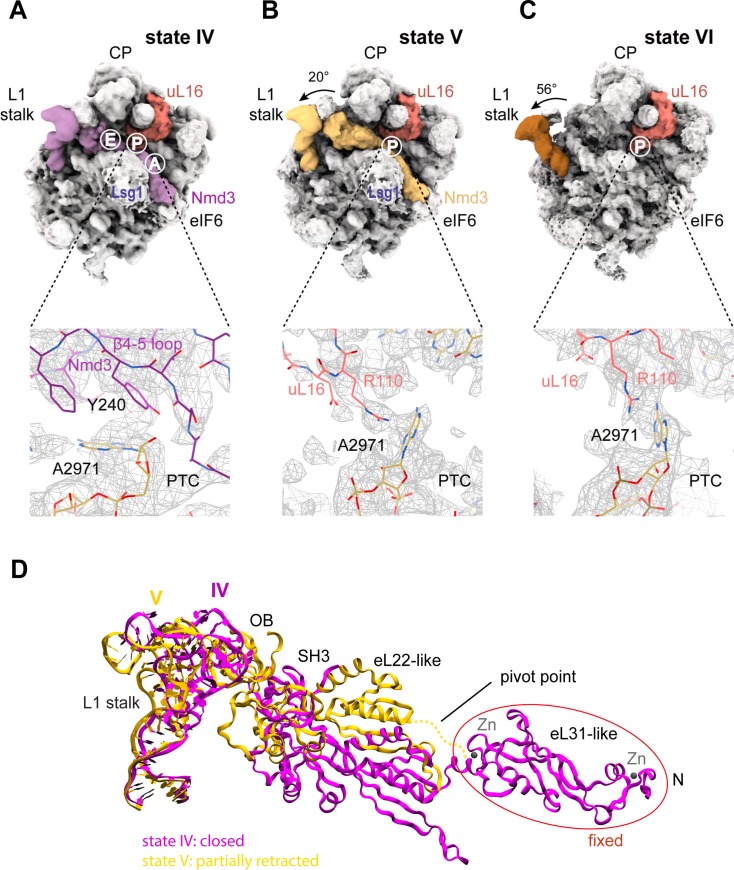
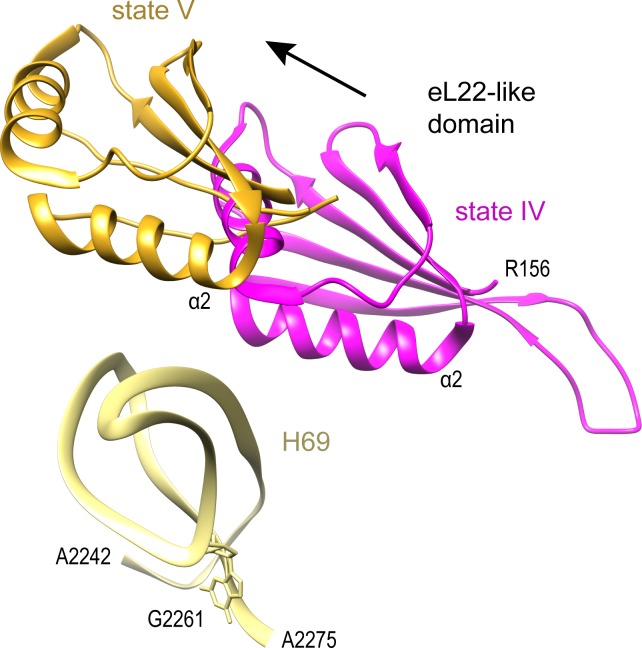
Figure 6. Mechanism of Nmd3 release.
(A) The Nmd3 β4–5 loop masks base A2971 (state IV). Insert shows base A2971 in the ‘closed’ position. H38 is ‘open’, the L1 stalk is ‘closed’ and uL16 is loaded. The A, P and E tRNA binding sites are indicated. (B) The uL16 P-site loop competes with the Nmd3 β4–5 loop for binding to base A2971 (state V). The L1 stalk is partially retracted (rotated by 20° relative to the fully closed L1 stalk); the Nmd3 β4–5 loop is displaced from the PTC. The uL16 P-site loop is bound to base A2971 in the flipped-out conformation. (C) The completed PTC (state VI). The L1 stalk is fully open (rotated by 56°), Nmd3 and Lsg1 have dissociated and the uL16 P-site loop is bound to base A2971 in the flipped-out conformation. (D) L1 stalk retraction promotes a conformational switch in the Nmd3 eL22-like domain. Atomic models for the L1 stalk and Nmd3 in states IV (magenta) and V (gold) are superimposed. The rotational pivot point between the eL31- and eL22-like domains is indicated.