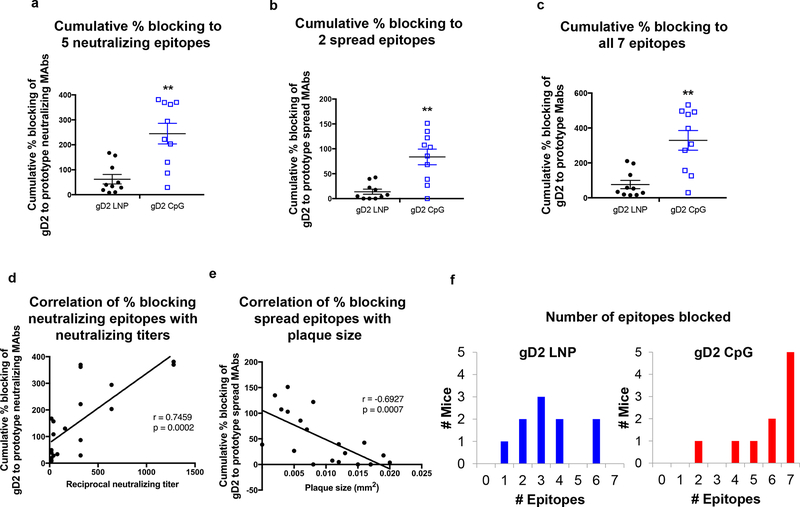
Figure 6. Blocking gD2 binding by prototype MAbs in each community and subcommunity.
(a) Cumulative percent blocking of gD2 binding by each mouse serum to (a) five prototype MAbs that bind to neutralizing epitopes, (b) two prototype MAbs that bind to cell-to-cell spread epitopes, and (c) all seven prototype MAbs that bind to neutralizing or cell-to-cell spread epitopes. Error bars in (a–c) represent SEM. (d) Correlation of neutralizing antibody titers of mice immunized with gD2 LNP-2 (n=10) or gD2 CpG/alum (n=10) with the cumulative percent blocking of antibodies produced to the five neutralizing epitopes. (e) Correlation of plaque size of mice immunized with gD2 LNP-2 (n=10) or gD2 CpG/alum (n=10) with the cumulative percent blocking of antibodies produced to the two cell-to-cell spread epitopes. (f) The number of epitopes blocked by mice in the gD2 LNP-2 or gD2 CpG/alum group. **, p<0.01; P values for (a-c) were calculated by the two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, (d–e) were calculated using Spearman’s correlation, and (f) by the two-tailed Fisher’s exact test (p=0.008).