Figure 1. Protection of green fluorescent protein (GFP) activity with polyepoxide crosslinkers.
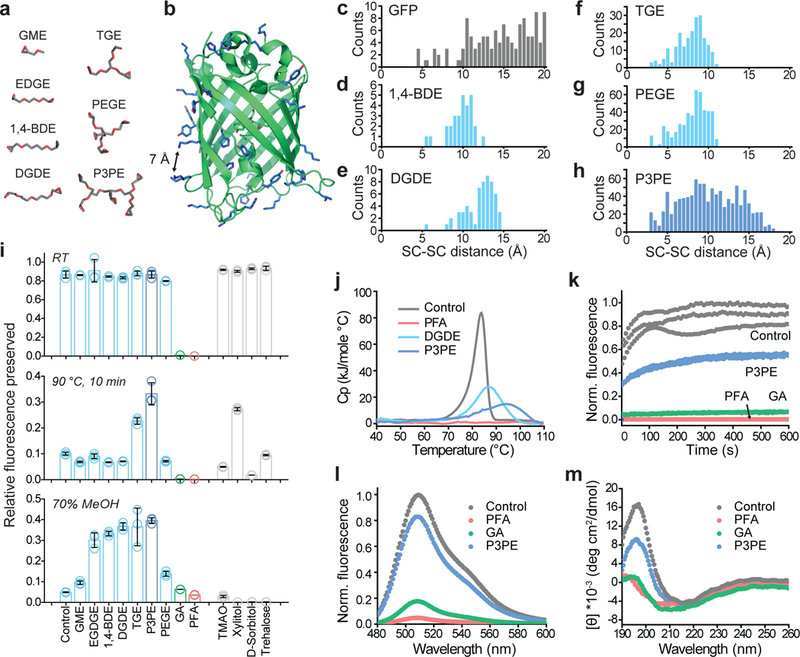
(a) Representative lowest-energy conformers of epoxide molecules, drawn at the same scale as b. (b) GFP structure, with epoxide-reactive residues labeled in blue. The black arrow indicates a 7-Å distance between side-chains. (c) Frequency count calculated for solvent-exposed GFP side-chains (SC) as a function of their pairwise distances. (d-h) Frequency count of the average distance between epoxide groups, determined from the lowest-energy epoxide conformers. (i) Degree of GFP fluorescence preserved after reaction with the crosslinker (top) followed by exposure to 90°C for 10 min (middle) or 70% methanol incubation for 1 hr (bottom). N=3 independent experiments. Mean +/− standard error mean was used for plotting this graph. (j) Differential scanning calorimetry plot of heat capacity as a function of the temperature of crosslinked GFP. (k) Plot of the fluorescence of crosslinked GFP recovered over time after renaturation from acid-denaturation. (l) Fluorescence spectra of crosslinked GFP. (m) Circular dichroism spectra of crosslinked GFP. GME, glycidyl methyl ether; EGDGE, ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether; 1,4-BDE, 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether; DGDE, dipropylene glycol diglycidyl ether; TGE, glycerol triglycidyl ether; PEGE, pentaerythritol polyglycidyl ether; P3PE, polyglycerol 3-polyglycidyl ether. PFA, paraformaldehyde; GA, glutaraldehyde. TMAO, trimethylamine N-oxide.
