Figure 4. SHIELD enables 3D imaging of various structures and cell-types and their morphological details in human brain tissue.
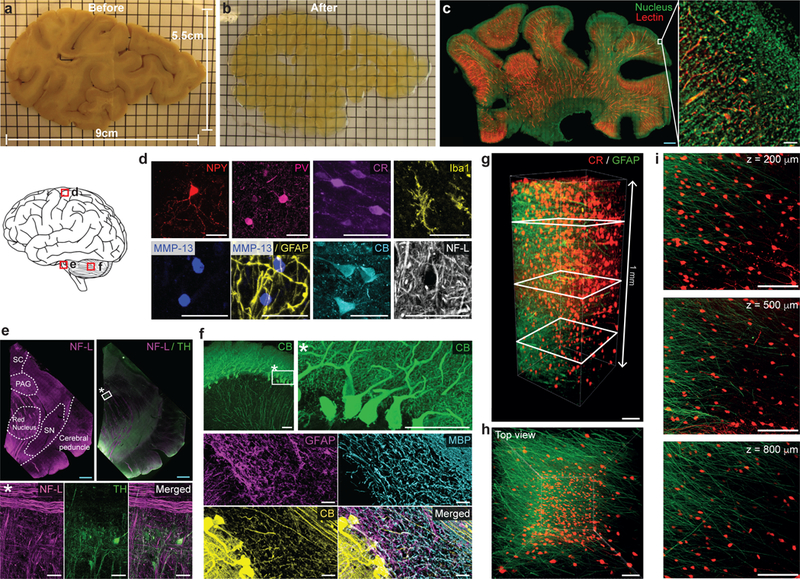
(a-b) 2 mm-thick slab of human brain coronal hemisphere (9 cm × 5.5 cm × 2 mm) before (a) and after (b) SHIELD processing. Grid = 5 mm. (c) A SHIELD-processed slab (22 mm × 38 mm × 1.3 mm) was stained with lectin and nuclear dye, and the 800μm-thick volume from the top surface was imaged with a custom-built temporally focused line-scanning two-photon microscope. Scale bars = 2 mm (blue) or 100 μm (white). See Supplementary video 3. (d-f) Immunostained cortex (d), midbrain (e), and cerebellum (f) from 100-μm-thick SHIELD-processed human brain tissues showing various cell-types and structures. In e, neurofilament-L (NF-L) staining assists delineation of midbrain areas. MMP-13, matrix metallopeptidase 13; SC, superior colliculus; PAG, periaqueductal gray; SN, substantia nigra; MBP, myelin basic protein; TH, tyrosine hydroxylase; Scale bar = 2 mm (blue) or 50 μm (white). (g-i) GFAP (green) and CR (red) immunolabeling of a SHIELD-processed 1 mm-thick human cortex coronal block. See Supplementary video 4. (g) 3D reconstruction. Scale bar = 100 μm. (h) Top view of the 3D reconstruction. Scale bar = 100 μm. (i) Maximum intensity projection images at various z-positions (200, 500, and 800 μm) marked by white rectangles in g. For maximum intensity projection, 100 μm-thick z-stacks were used at each z-position. Scale bar = 100 μm.
