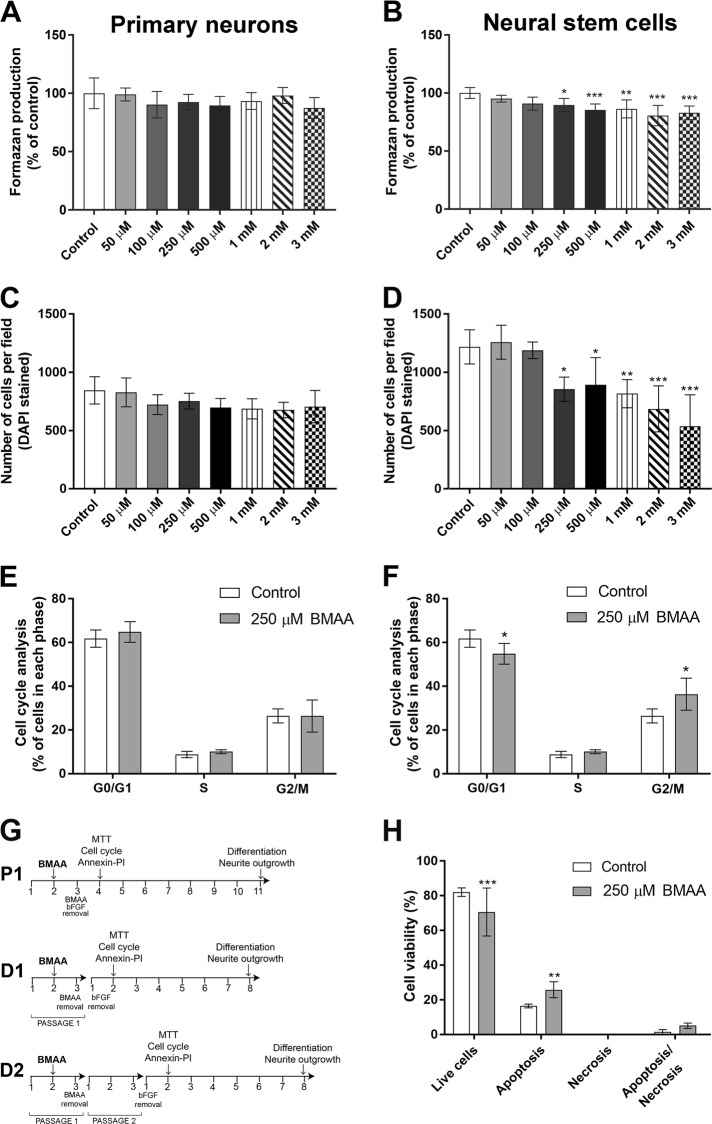
Fig. 1. Effects of BMAA on cell viability and proliferation in striatal primary neurons and neural stem cells.
Cell viability was determined by the MTT assay (a, b) and proliferation by DAPI staining (c, d) after treatment with 50 µM to 3 mM for 24 h. The cell cycle phase of cells treated with 250 µM BMAA was analyzed by flow cytometry (e, f). Apoptotic and necrotic cells were assessed with the annexin V and PI assay in cells treated with 250 µM BMAA (h). Apoptotic cell death was detected with 488-labeled annexin V; necrotic cells were detected with PI; cells that underwent apoptosis followed by necrosis were detected with annexin plus PI; and cells without labeling were live cells. The experimental design used for investigating BMAA effects on NSC (g). NSC were cultured for 3 days before passaging to obtain parent cells (P1). After 1 day in culture, P1 were exposed to BMAA for 24 h. To investigate mitotically inherited long-term effects of BMAA, P1 cells were passaged to daughter cells (D1 and D2). Values represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments, each with six replicates. Statistically significant differences from control are indicated as follow: ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–kramer test)