Table 2.
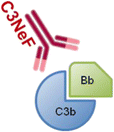
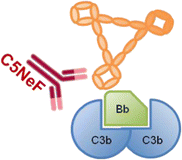
Proposed underlying mechanisms in the pathophysiology of C3 glomerulopathy based on the presence of different types of convertase-stabilizing nephritic factors
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Type of C3NeF | Properdin-independent C3NeF | Properdin-dependent C3NeF/C5NeF |
| Associated complement profile | C3 consumption | C3 consumption |
| C5 normal or slightly consumed | C5 consumption | |
| sC5b-9 normal | sC5b-9 elevated | |
| Disease association | DDD | C3GN |
| Comparative mouse model | FH−/−/P−/− | FH−/− |
C3NeF C3 nephritic factor, C5NeF C5 nephritic factor, sC5b-9 soluble C5b-9, DDD dense deposit disease, C3GN C3 glomerulonephritis, FH factor H, P properdin
