Figure 2.
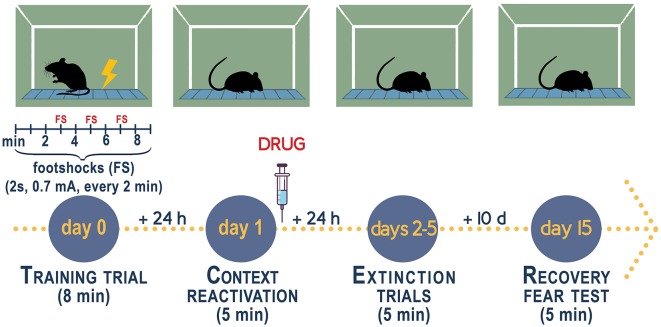
Experimental procedure to measure fear conditioning responses, fear extinction, and fear extinction retention in socially isolated mice. Contextual fear conditioning responses in socially isolated is studied after 4 weeks of isolation when the decline of allopregnanolone is maximal (Pibiri et al., 2008; Pinna et al., 2008). Group-housed mice of the same age as the socially isolated mice serve as control. Socially isolated mice express a decrease of corticolimbic allopregnanolone levels that is associated with an enhancement of contextual fear responses and impaired fear extinction (Pibiri et al., 2008). The fear-conditioning apparatus, which schematized in the figure, consists of a transparent acrylic chamber measuring 25 cm wide, 18 cm high, and 21 cm deep (San Diego Instruments). The cage floor is composed of stainless-steel rods connected to an electric shock generator. A small fan is located on the top wall of the enclosure. The chamber is surrounded by a frame with 16 infrared photo beams. A computer controls the delivery of electric foot shocks and auditory stimuli and records beam interruptions and latencies to beam interruptions (freezing time). Training Test. During the training, mice are placed into the training chamber and allowed to explore it for 2 min. After this time, they receive an unconditioned stimulus (US, electric footshock, 2 s, 0.5 mA). The footshock is repeated three times every 2 min. After the last tone plus shock delivery, mice are allowed to explore the context for an additional minute before removal from the training chamber (total of 8 min). Contextual Test. Twenty-four hours after training, the mice are placed in the contextual cage, and freezing behavior is measured for 5 min (Freeze Monitor System, San Diego Instruments) without footshock presentation. Extinction Test. For contextual extinction experiments, mice are placed in the contextual cage for 5 consecutive days starting 24 h after the training session. Fear extinction retention. Retention of fear extinction is measured by placing the mice to the context for 5 min following an interval of 10 days. Freezing behavior is measured for 5 min without tone or footshock presentation. Freezing is defined by the absence of any movement except for those related to respiration while the animal is in a stereotypical crouching posture (Pibiri et al., 2008). To disrupt aversive memories through a reconsolidation blockade (Stern et al., 2012), drugs are given immediately after a contextual fear conditioning reactivation session (Pinna and Rasmusson, 2014; Locci and Pinna, 2019b).