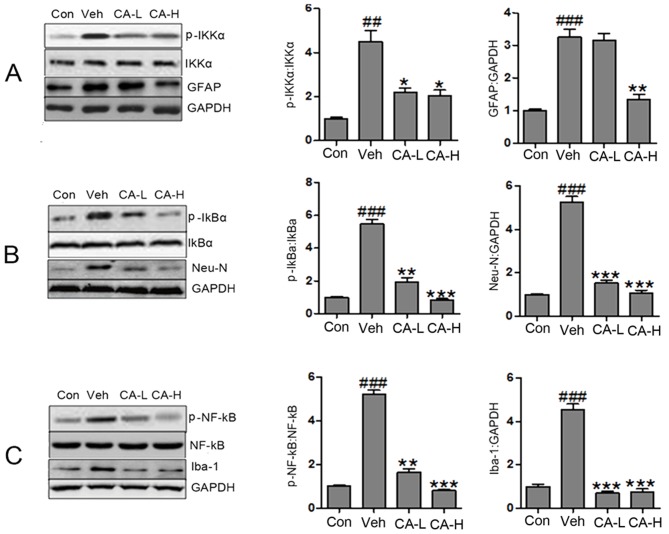
Figure 4.
CA attenuates brain injury in HFD mice by inactivating the NF-κB signaling pathway. (A) Protein expression levels of p-IKKα, IKKα, GFAP and GAPDH in different groups, as assessed by western blot analysis. (B) Protein expression levels of p-IκBα, IκBα, Neu-N and GAPDH in different groups, as assessed by western blot analysis. (C) Protein expression levels of p-NF-κB, NF-κB, Iba-1 and GAPDH in different groups, as assessed by western blot analysis. Data are expressed as the means ± SEM. n=10 in each group. ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs. Con; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. Veh. CA, carnosic acid; CA-H, HFD mice treated with 20 mg/kg CA; CA-L, HFD mice treated with 10 mg/kg CA; Con, Control group; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; HFD, high-fat diet; IκBα, NF-κB inhibitor α; IKKα, IκB kinase α; Neu-N, neuronal nuclei; Iba-1, ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1; p, phosphorylated; Veh, HFD mice.