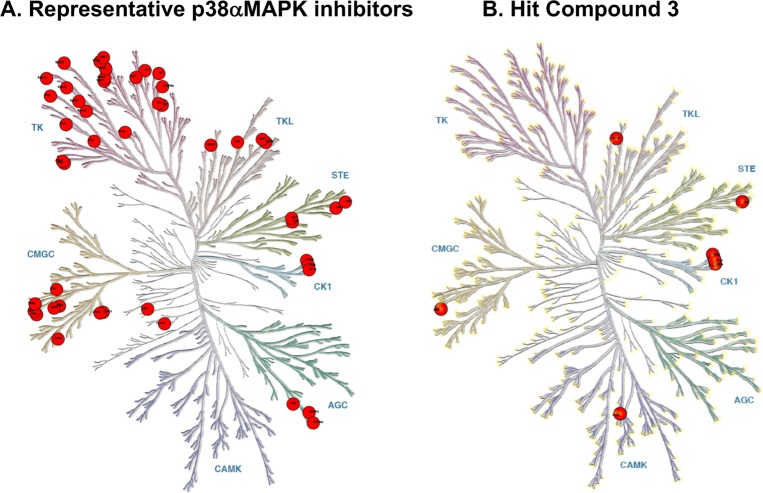
Figure 3.
Kinome target selectivity of hit compound 3 vs off-target kinases of widely used p38MAPK inhibitors. Red circles denote inhibition at specific kinases with IC50 < 1 μM. (A) Kinase inhibition profile for the widely used p38αMAPK inhibitors VX-745, BIRB-796, and SB203580.24−26 Crossover kinases with IC50 < 1 μM for VX-745 include ABL1, ABL2, p38β, PDGFRβ, SRC; for BIRB-796 include BLK, CDK5, CDK8, DDR1, DDR2, EPHA3, EPHA7, EPHA8, EPHB2, p38β p38γ, FLT1, FRK, NTRK1, JNK1, JNK2, JNK3, KIT, MAP4K4, MRCKβ, PTK2β, RET, SLK, STK10, TIE1, TIE2, TNIK, TRKB, TRKC, ZAK; and for SB203580 include BRAF, CIT, CK1δ, CK1ε, DMPK, GAK, JNK2, JNK3, NLK, p38β, RIPK2, STK36, TNIK. (B) Kinase targets (IC50 < 1 μM) for compound 3 (Table 4S). Crossover kinases with IC50 < 1 μM for compound 3 include CK1α, CK1δ, CK1ε, PKD3, RIPK2, and TNIK.