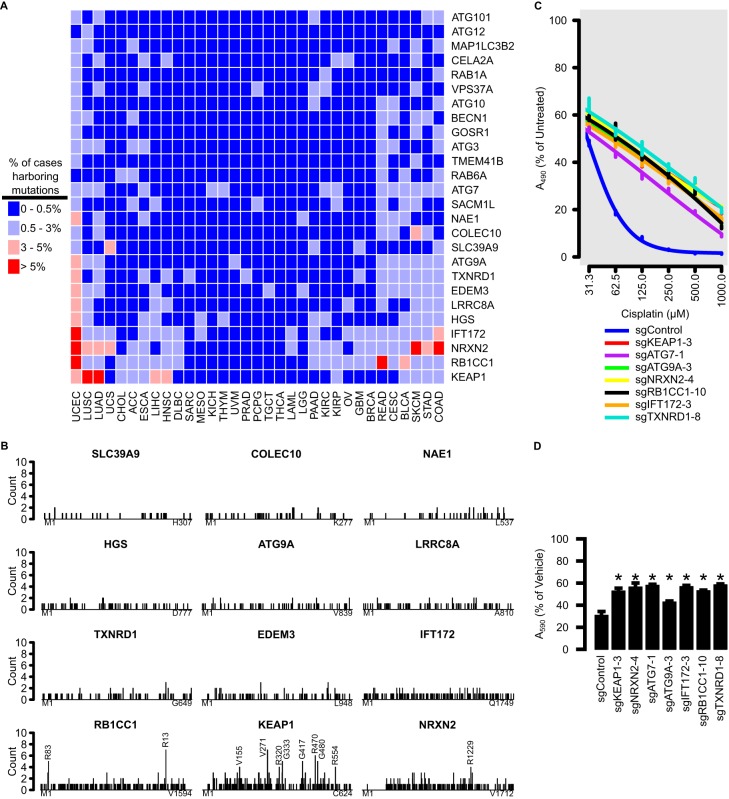
FIG 7.
Mutations to genes identified by CRISPR screen are found in cancer and may contribute to chemoresistance. (A) TCGA cases were stratified by tumor types for frequencies of mutations to genes identified by the CRISPR screen. Colors represent percentages of cases harboring mutations to that gene, within tumor type. (B) Frequency of amino acid mutations along the lengths of the top 12 most frequently mutated genes identified by CRISPR screen. Mutation spread along the length is indicative of a tumor suppressor. Positions harboring 4 or more mutations are annotated. (C) Twenty-four-hour cisplatin dose response of HK2 cells harboring various gene knockouts, as measured by MTS assay. (D) Cell viability assay of HK2 cells with various gene knockouts treated with 50 μM cisplatin, as measured by crystal violet assay. Error bars represent standard deviation of 3 biological replicates, and asterisks represent groups that were statistically significantly different from the control, as determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the post hoc Tukey test.