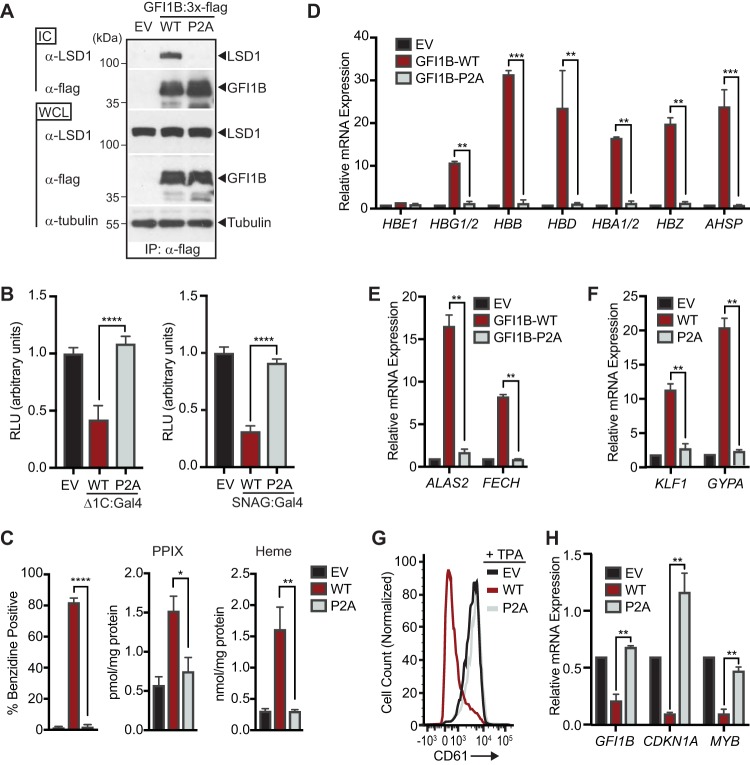
FIG 2.
LSD1 binding is required for GFI1B-regulated cell fate decisions in K562 cells. (A) P2A substitution in GFI1B impairs GFI1B-LSD1 binding. K562 cells were transduced with constructs expressing wild-type GFI1B:3×-Flag, its P2A variant, or empty vector (EV) as shown. GFI1B forms were immunopurified with anti-Flag (M2) antibody and protein G-Sepharose. LSD1 was quantified in immune complexes (ICs) by Western blotting. Equal expression (LSD1 and GFI1B) and precipitation (GFI1B) were evaluated by Western blotting of whole-cell lysates (WCLs) and ICs, respectively. Tubulin was used to confirm equal gel loading. (B) P2A substitution abolishes transcriptional repression by GFI1B. 293-T-Rex-5×Gal-luciferase cells were transfected with WT or P2A variants of GFI1B-Δ1C:Gal4 (left) or SNAG:Gal4 (right) fusion proteins. Firefly luciferase was measured and normalized to constitutively expressed, cotransfected Renilla luciferase. Reporter activity is expressed as mean ± 2 SD from two experiments performed in triplicate. (C) P2A substitution impairs GFI1B-mediated hemoglobinization. Benzidine staining was quantified as for Fig. 1A. Protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) and heme were quantified by UPLC in K562 cells transduced with EV, GFI1B-WT, or GFI1B-P2A. (D to F) P2A substitution impairs expression of erythroid fate genes in K562 cells. Expression of anti-globin cluster genes AHSP, ALAS2, FECH, GYPA, and Kruppel-like factor 1 gene (KLF1) are shown. (G) P2A substitution abolishes GFI1B-mediated suppression of TPA-induced CD61 expression. Cell surface expression of CD61 in TPA-treated cells expressing GFI1B-WT or its P2A variant was determined by flow cytometry. (H) P2A substitution reverses repression of GFI1B target genes GFI1B, CDKN1A, and MYB. Results expressed as mean ± 2 SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005; ****, P < 0.00005.