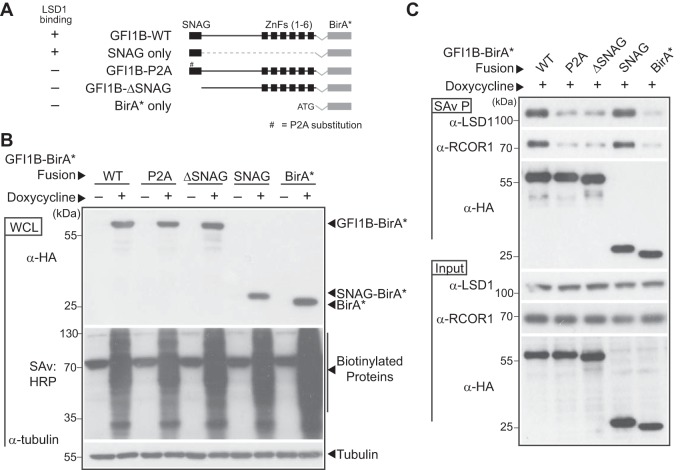
FIG 6.
LSD1-nonbinding variants of GFI1B-BirA*:HA fail to biotinylate LSD1 and RCOR1. (A) Graphical representation of GFI1B-BirA*:HA fusion proteins employed in experiments. Each fusion protein is comprised of the GFI1B regions shown in frame with the BirA* expression cassette and a C-terminal HA epitope tag to ensure equivalent expression of all forms. The BirA*:HA construct lacks GFI1B structures and instead begins with an ATG. Wild-type (WT) GFI1B is shown. The SNAG and zinc finger (ZnF) domains (1 to 6) of GFI1B are shown as black boxes. A thin line represents the GFI1B linker and connections between ZnFs. The proline-to-alanine substitution (P2A) in the GFI1B SNAG domain is indicated. ΔSNAG represents deletion of the SNAG domain but preservation of the remaining GFI1B primary structure. (B) Expression of GFI1B-BirA*:HA forms and proteome-wide biotin modification in K562 cells. K562 cells were transduced with lentivirus to inducibly express the GFI1B-BirA*:HA forms shown and stable isolates selected as polyclonal populations. Doxycycline-inducible expression of each fusion protein was confirmed by Western blotting against the common HA epitope tag and biotinylating activity confirmed proteome-wide by SAv:HRP detection of transblotted total cellular protein. Tubulin served as a loading control. (C) LSD1 and RCOR1 are enriched among biotinylated proteins generated by BirA*:HA fusions competent for LSD1 binding. Biotin-modified proteins from K562 cells transduced with the BirA*:HA fusion proteins shown were purified from whole-cell extracts (SAv P), fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and subjected to Western blotting with anti-LSD1, anti-RCOR1, and anti-HA antibodies. Equivalent expression of each protein in whole-cell lysates (input) was confirmed by Western blotting with these same antibodies.