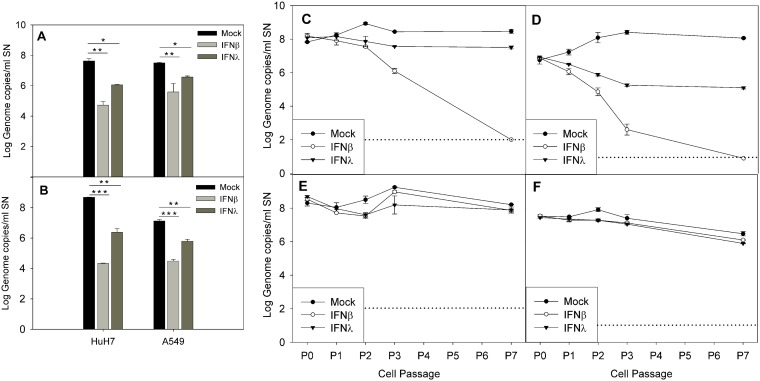
FIG 9.
Effect of exogenous IFN during acute infection (A and B) and in persistently infected cultures (C to F). (A and B) Effect of exogenous IFN-β1a and IFN-λ1 on acutely infected Huh-7AI and A549 cells by MLB1 (A) and MLB2 (B). The graphic illustrates the mean viral titer measured in the supernatant at 4 dpi, and error bars show one standard deviation. There was a statistically significant difference in the viral titer between no IFN and IFN-β1a and between no IFN and IFN-λ1 (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.001, ANOVA and Scheffe tests). (C to F) Effect of exogenous IFN-β1a and IFN-λ1 on Huh-7AI cultures persistently infected with MLB1 (C) or MLB2 (D) and on A549 cultures persistently infected with MLB1 (E) and MLB2 (F). Data represent the mean ± standard deviation titer of viral RNA in the supernatant of each passage measured at 4 to 6 days postseeding in the presence or absence of exogenous IFN-β1a or IFN-λ1. All passages were performed in duplicate. P0 corresponds to the viral titer at 1 day after seeding of the first passage with exogenous IFN. Dotted line indicates the limit of detection. P, passage; SN, supernatant.