Figure 4.
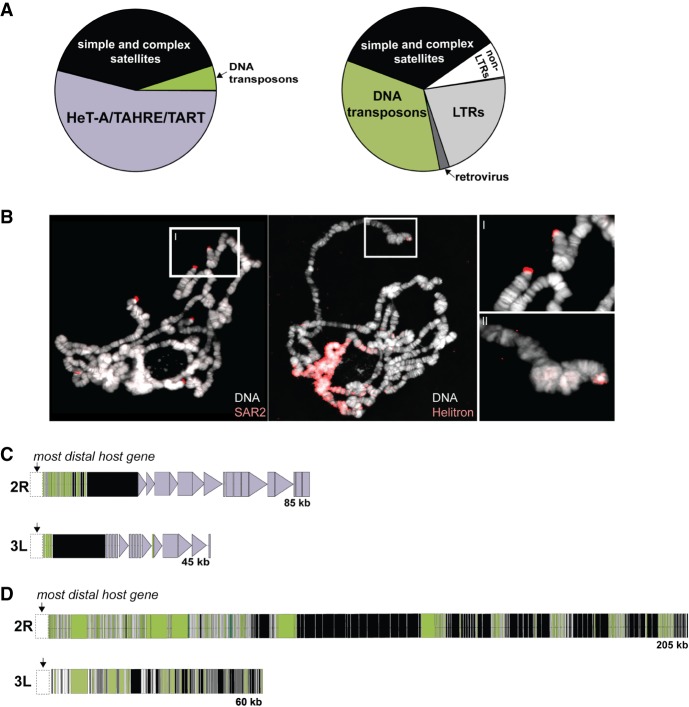
Collapse of the retrotransposon-based telomere elongation mechanism in D. biarmipes. (A) Composition of D. melanogaster and D. biarmipes chromosomes between the most distal, protein-coding gene and the terminal nucleotide. Fractions estimated from the distal sequence (assembled from PacBio-generated long reads for both species) for Muller elements corresponding to 2L, 2R, 3L, and 3R. Purple corresponds to telomere-specialized, jockey family retrotransposons found in D. melanogaster (but not in D. biarmipes). (B) Fluorescent in situ hybridization of SAR2 and Helitron probes to polytene chromosomes from D. biarmipes. Insets I and II show telomere localization of SAR2 and Helitrons, respectively, on D. biarmipes polytene chromosomes. (C) Schematic representation of the long-read–based assembly of D. melanogaster 2R and 3L telomeric DNA. Telomere-specialized, jockey-like elements (purple) are distal to a block of simple and complex satellites (black), consistent with previous reports. Triangles represent full-length elements, and rectangles represent partially degenerated elements. (D) Schematic representation of the long read–based assembly of 2R and 3L telomeres from D. biarmipes in which simple and complex satellite DNA (black) is juxtaposed with primarily Helitron DNA transposons (green).