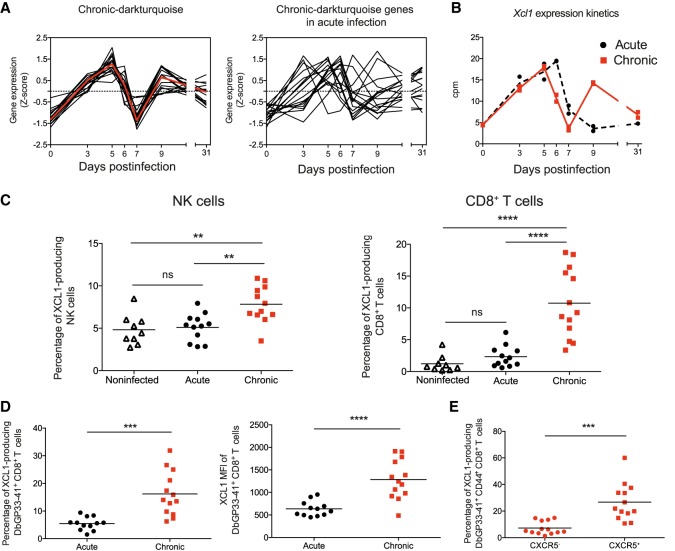
Figure 6.
Chronic-darkturquoise-specific module reveals an important role of XCL1 in chronic infection. (A) Normalized expression kinetics of genes from the chronic-darkturquoise module and their corresponding kinetics in acute infection. (B) Xcl1 expression kinetics obtained from RNA-seq analysis. (C) Percentages of XCL1-producing NK and CD8+ T cells at day 9 PI. Data shown are the mean ± SEM from n = 11 to 13 mice representative of three independent experiments (significance determined using one-way ANOVA). (D,E) MFI of XCL1 in DbGP33-41+ CD8+ T cells (D, right) and percentages of XCL1-producing DbGP33-41+ CD8+ T cells (D, left) and CXCR5- or CXCR5+ DbGP33-41+ CD44+ CD8+ T cells (E) at day 9 PI. Data shown are the mean ± SEM from n = 11 to 13 mice (significance determined using unpaired two-tailed t-test). (ns) not significant; (**) P ≤ 0.01; (***) P ≤ 0.001; (****) P ≤ 0.0001.