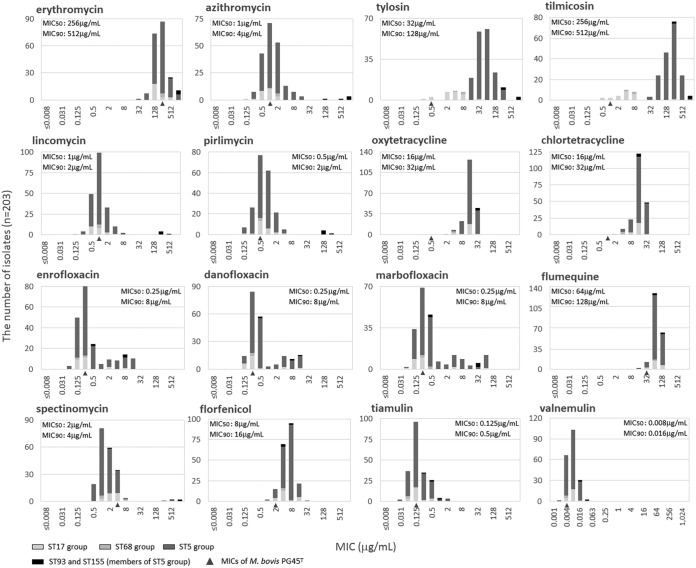
FIG 2.
Relationship between antimicrobial susceptibility distribution and genotypes by MLST of M. bovis field isolates in Japan. MIC values of strain PG45T are indicated with a triangle under the bar graph. M. bovis showed natural resistance to erythromycin and flumequine. Isolates of ST93 (a member of the ST5 group) showed low susceptibility to spectinomycin, macrolides, lincosamides, tetracyclines, and fluoroquinolones. Moreover, isolates of ST155 (a member of the ST5 group) showed low susceptibility to macrolides, lincosamides, and tetracyclines. Although ST14 (a member of the ST68 group) and isolates in the ST17 group (oldcomer) showed high susceptibility to 16-membered macrolides, ST68 and isolates in the ST5 group (newcomer) showed low susceptibility to these agents. Susceptibility to tetracyclines was on a declining trend overall. Isolates that showed low susceptibility to fluoroquinolones emerged sporadically, and their ST groups were varied. On the other hand, susceptibility to pleuromutilins was high, and no isolate with low susceptibility was found.