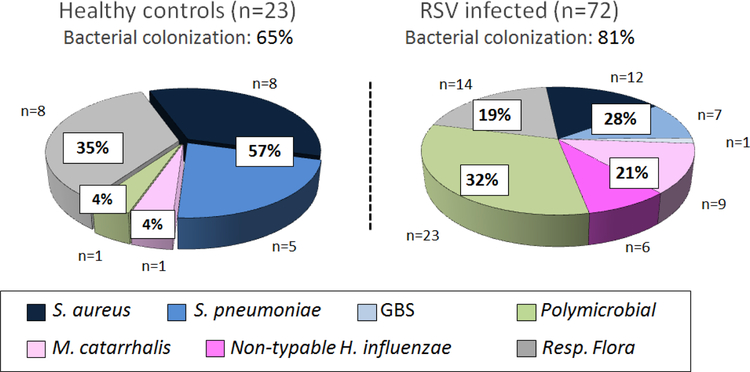
Figure 2. Percentage and type of potentially pathogenic bacteria colonizing the nasopharynx in healthy controls and infants hospitalized with RSV LRTI.
We enrolled a cohort of previously healthy infants with RSV LRTI and age-matched healthy asymptomatic controls. Nasopharyngeal samples were obtained within 24h of hospitalization and potentially pathogenic bacteria identified by culture. Respiratory flora included the normal bacterial flora colonizing the upper respiratory tract. Pie charts represent the percentage of respiratory flora, gram positive, gram-negative bacteria and >1 PPB present in NP samples from these healthy infants and infants with RSV LRTI not treated with antibiotics. (Reproduced with permission from ref. 6)