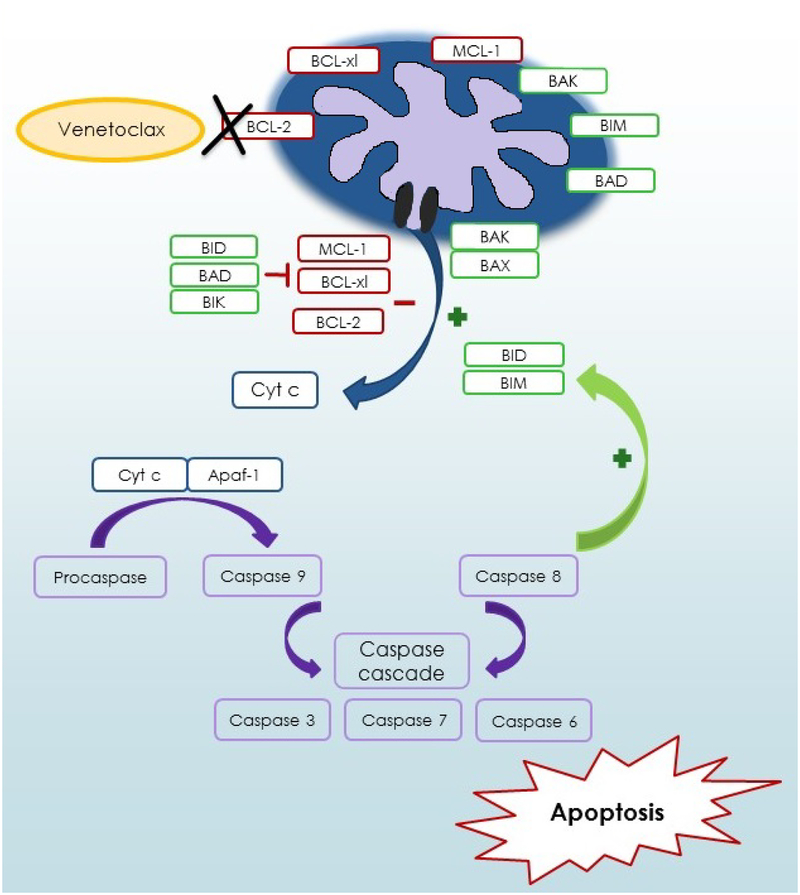
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and venetoclax mechanism of action. In response to cellular stress, the pro-apoptotic proteins BAX and BAK are translocated to the mitochondria and induce the permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane with release of cytochrome c (Cyt C) into the cytoplasm. The Cyt C/Apaf-1 complex activates caspase 9 and the caspase cascade, inducing apoptosis. The mitochondrial pathway is regulated by pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins, which activate BAX and inhibit BCL-2 and MCL-1. BCL-2, MCL-1 and BCL-X regulate cell survival by inactivation of the pro-apoptotic proteins. Venetoclax triggers apoptosis by selective inhibition of BCL-2, leading to the release of Cyt C and cell death.