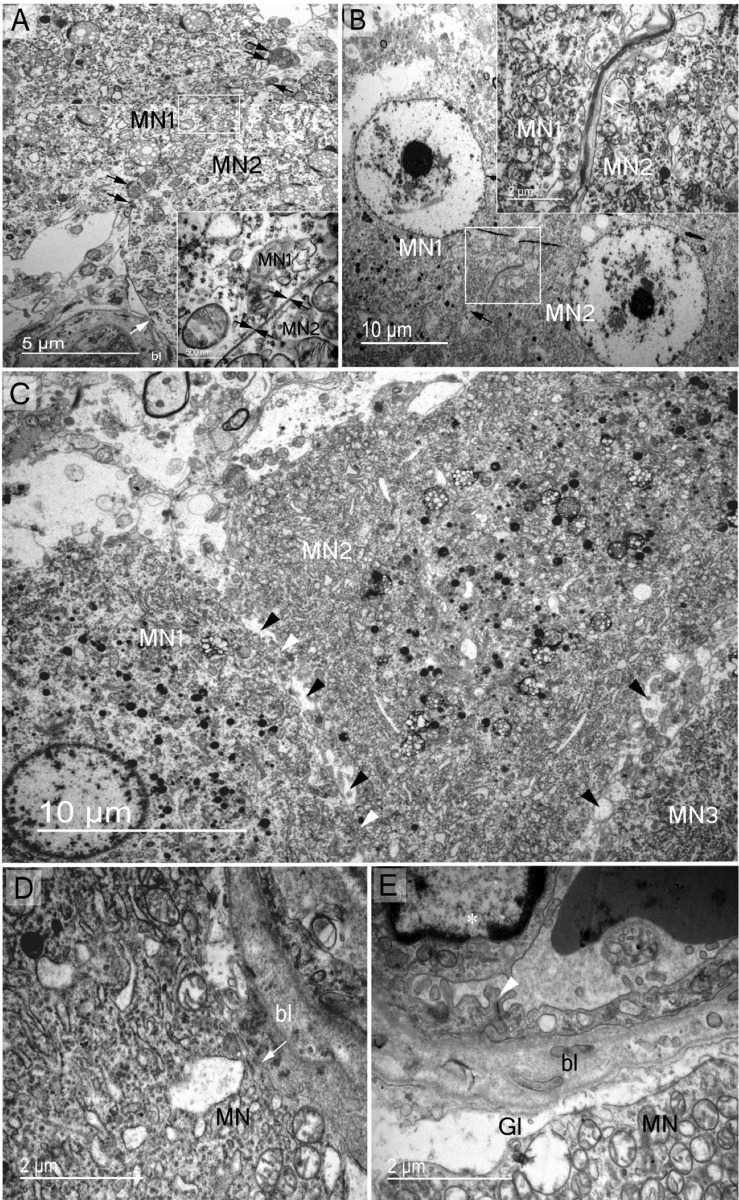
Fig 5. Structural membrane contacts of somatic zone magnocellular perikaryons.
Magnocellular neurones establish different types of membrane contact with other supraoptic nucleus elements. (A) Soma-somatic membrane apposition of two adjacent magnocelluar neurones (MN1 and MN2) without intervening neuropil elements; MN1 and MN2 membranes in close contact (arrows in magnified rectangle). Note the presence of active synapses on both MNs (dark arrows). Direct contact of magnocellular neurone membrane with the basal lamina (bl) of a capillary (light arrow). (B) Two adjacent magnocellular neurones (MN1 and MN2) membranes separated by neuropil elements (arrow in the square magnified). (C) Adjacent magnocellular neurones (MN1, MN2 and MN3) with direct soma-soma membrane apposition (white arrowheads between MN1 and MN2) and separated by neuropil elements in several places (dark arrowheads). (D) Direct contact of MN soma membrane with capillary basal lamina (bl) (arrow). (E) Blood barrier in the supraoptic nucleus demonstrating endothelial cells (asterisk) tightly linked (arrowhead) and magnocelluar neurone membrane separated from capillary basal lamina by glial process (Gl).