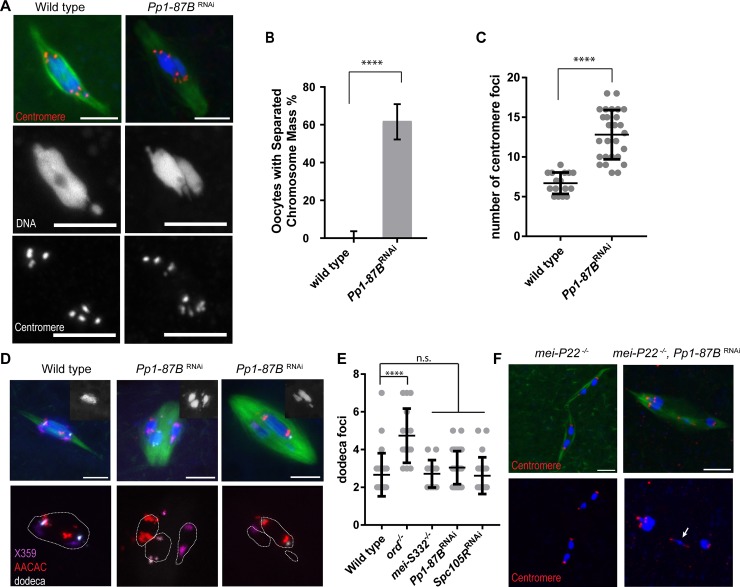
Fig 1. Pp1-87B RNAi oocytes have defects in chromosome mass organization and sister centromere fusion.
(A) Pp1-87B RNAi oocytes show separated chromosome mass and sister centromere (red) separation in metaphase I with tubulin in green and DNA in blue. DNA and centromeres are shown in separate channels. In wild-type, the fourth chromosomes sometimes appear as a dot separated from the chromosome mass. Scale bars indicate 5 μm. (B) Quantification of the separated chromosome mass phenotype in wild-type (n = 20) and Pp1-87B RNAi oocytes (n = 50). **** = p < 0.0001. Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval. (C) Quantification of centromere foci. Error bar shows standard deviation. Number of oocytes: wild type n = 16 and Pp1-87B RNAi n = 27. **** = p < 0.0001, (D) Chromosome mass separation defect in Pp1-87B RNAi oocytes. DNA channel is shown in the inset. FISH probes for the X (359 bp repeat, purple), 2nd (AACAC, red) and 3rd chromosome (dodeca, white) were used to detect pericentromeric heterochromatin. The chromosome mass is outlined in white. Two examples are shown of Pp1-87B RNAi oocytes with homologs bi-oriented and not bi-oriented. Scale bars are 5 μm. (E) Quantification of dodeca foci to detect precocious separation of pericentromeric heterochromatin. Number of oocytes: wild-type (n = 27), ord (n = 15), mei-S332 (n = 14), Pp1-87B RNAi (n = 50) and Spc105R RNAi (n = 21). **** = p < 0.0001. (F) Recombination defective mutant mei-P22 displayed homologous chromosome separation indicting precocious anaphase I in oocytes normally arrested in metaphase I. Knocking down Pp1-87B in a mei-P22 mutant background resulted in sister chromatid bi-orientation in meiosis I (arrow). The bioriented univalent can be identified because it has not segregated to a pole like the other univalents. In addition, it is the only chromosome where the centromeres are oriented towards opposite poles. And given that there are no chiasmata, the only linkage between these two centromeres can be pericentromeric cohesion of sister chromatids.