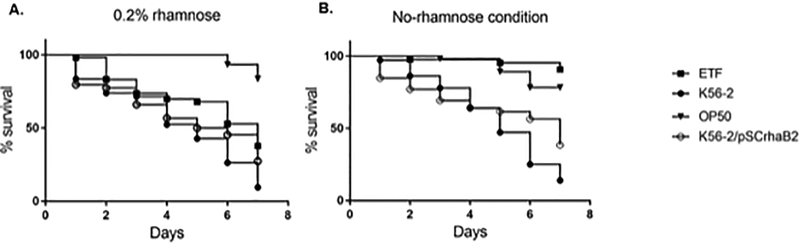
Figure 1.
Liquid killing assays. C. elegans was allowed to feed for 16 hours on B. cenocepacia K56–2, E. coli OP50 (non-pathogenic control), or the B. cenocepacia CGetf mutant (ETF) in the presence of 0.2% rhamnose to mimic WT levels of etf expression. Twenty to 30 worms were added to 96-wells plates containing 100 μl of liquid killing medium with (A) or without (B) the presence of 0.2% rhamnose. Four wells were inoculated per condition. The number of worms was counted every 24 hours for 7 days and plotted as survival curves using GraphPad Prism. K56–2 carrying the plasmid pSCrhaB2, which confers resistant to trimethoprim, was included as a control.