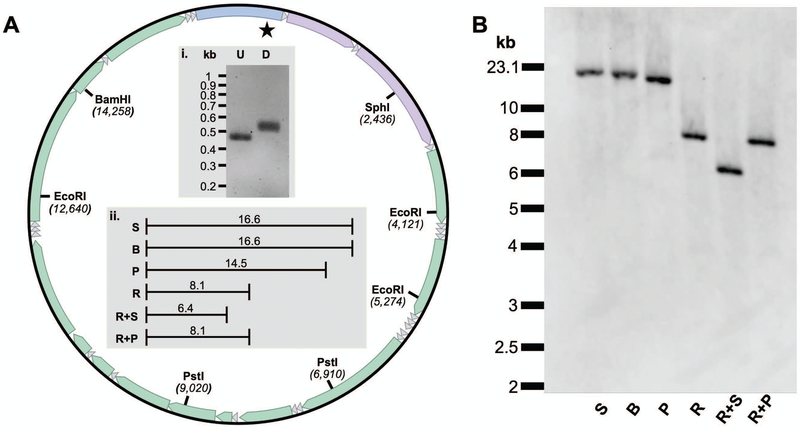
Fig. 1.
Restriction endonuclease mapping of the human mtDNA genome utilizing the mtDNA-specific DIG-labeled probe. A. Map of mtDNA highlighting the location and position of key restriction endonuclease (RE) sites. The star represents the binding site for the probe and the 22 small triangles represent the mitochondrial tRNA genes. The remaining features on the mtDNA map going clockwise from the top of the circle include the control region (with heavy-strand origin of replication and displacement-loop), followed by genes coding for 12 S rRNA, 16 S rRNA, NADH dehydrogenase (ND) 1, ND2, cytochrome oxidase (COX) I, COXII; ATPase 8, ATPase 6, COX III, ND3, ND4L, ND4, ND5, ND6 and, cytochrome b. i. A 1.2% agarose gel with unlabeled (U) control and DIG-labeled (D) PCR products generated using the mt168F and mt604R primer set. ii. Expected kilobase pair (kb) fragment lengths following RE digestion. Numbering and RE sites are based on the 16.569 kb human reference sequence, NC_012920.1. B. A representative Southern blot of HepaRG whole-cell DNA samples separately digested with key REs. Both the exACTGene™ DNA Ladder and Lambda DNA/HindIII Marker, 2 were run alongside the samples. The migration distances of the 23.1 kb lambda fragment and the 10 to 2 kb exACTGene fragments are emphasized on the left-hand-side of the blot. S, SphI; B, BamHI; P, PstI; R, EcoRI, R + S, EcoRI & SphI; R + P, EcoRI & PstI. Note, S and B only cut once within mtDNA generating a genome length fragment.