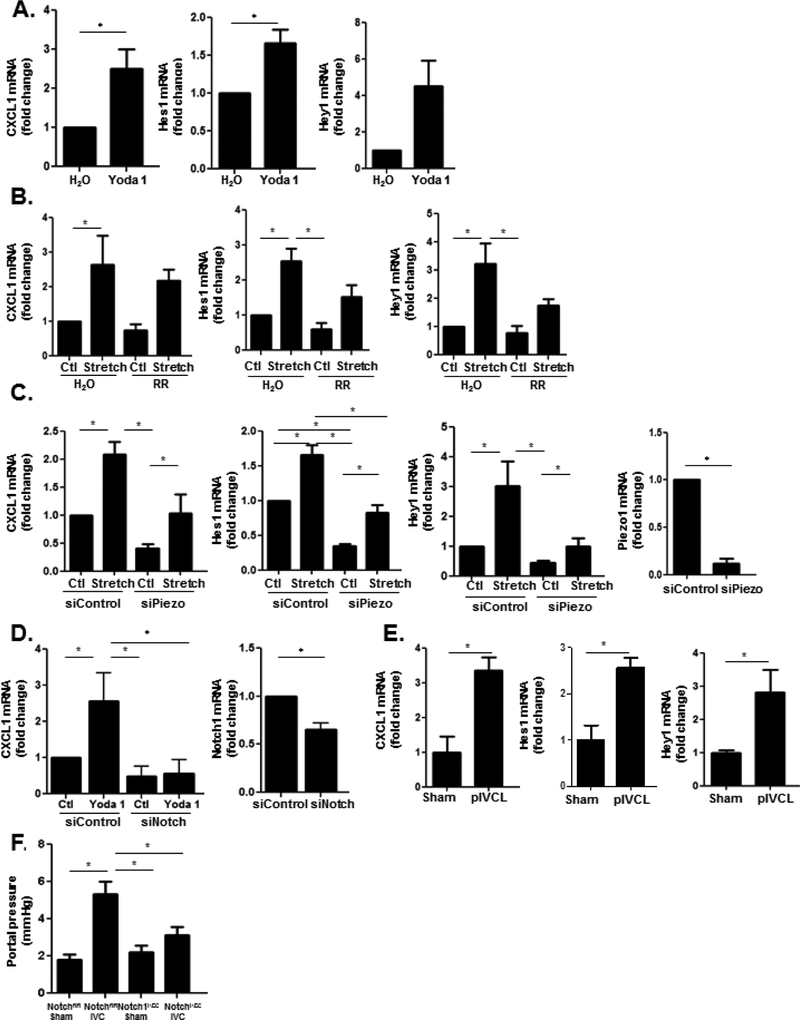
Figure 6. Notch pathway interacts with piezo1 channels to upregulate CXCL1.
(A) Stimulation of HUVEC with the piezo1 activator Yoda1 increases mRNA levels of Hes1, Hey1, and CXCL1. (B) Inhibition of piezo1 channels with ruthenium red decreases mRNA levels of CXCL1, Hes1, and Hey1 in HUVEC (CXCL1 ANOVA P≤0.05; Hes1 ANOVA P≤0.05; Hey1 ANOVA P≤0.05). (C) Transfection of HUVEC with siRNA pool to piezo1 decreases upregulation of CXCL1 as well as the Notch targets, Hes1 and Hey1, by cyclic stretch (Hey1 ANOVA P≤0.05; Hes1 ANOVA P≤0.05; CXCL1 ANOVA P≤0.05). siRNA knockdown of piezo1 is shown. (D) Transfection of HUVEC with siRNA pool to Notch1 attenuates the upregulation of CXCL1 by Yoda1 (P≤0.05). siRNA knockdown of Notch1 is shown. (E) Primary LSECs were isolated from mice 48 hours after pIVCL and sham procedures. Quantitative reverse transcription PCR showed increased mRNA levels of Hes1, Hey1, and CXCL1in primary LSECs after IVC ligation compared to sham controls (n=3–5, *P≤0.05 for all panels). (F) Mice with LSEC-specific deletion of Notch1 (Notch1iΔEC) have lower portal pressures when compared with Notchfl/fl mice 4 weeks after IVC ligation (n=7–11; ANOVA P≤0.05).