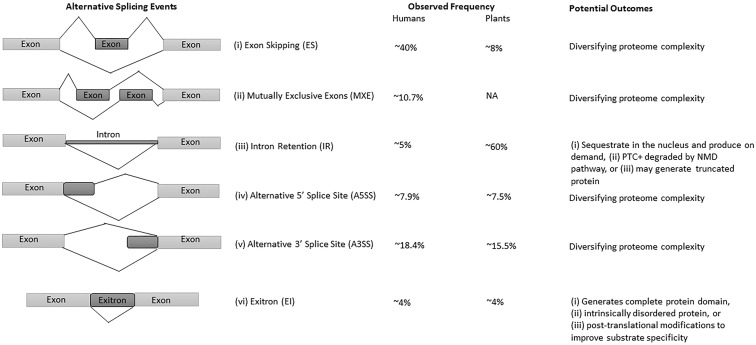
FIGURE 1.
Major types of AS events, their frequency, and potential outcomes in humans and plants. (i) exon skipping (ES) or cassette exon, in which single or multiple exons are spliced out or retained; (ii) mutually exclusive exons (MXE), in which only one of the two exons is retained; (iii) intron retention (IR), where an intron remains in the mature transcript; (iv, v) alternative donor/acceptor site or 5′/3′ splice junction is used to alter the boundary of exons, and (vi) exitrons are a variety of IR with some feature of exons. Constitutive and alternatively spliced exons are represented as light and dark gray blocks, respectively. The observed frequencies represented here are approximate values, and may differ in different species, tissues and conditions. The presented data on AS events frequency are from Reddy et al. (2013), Marquez et al. (2015).