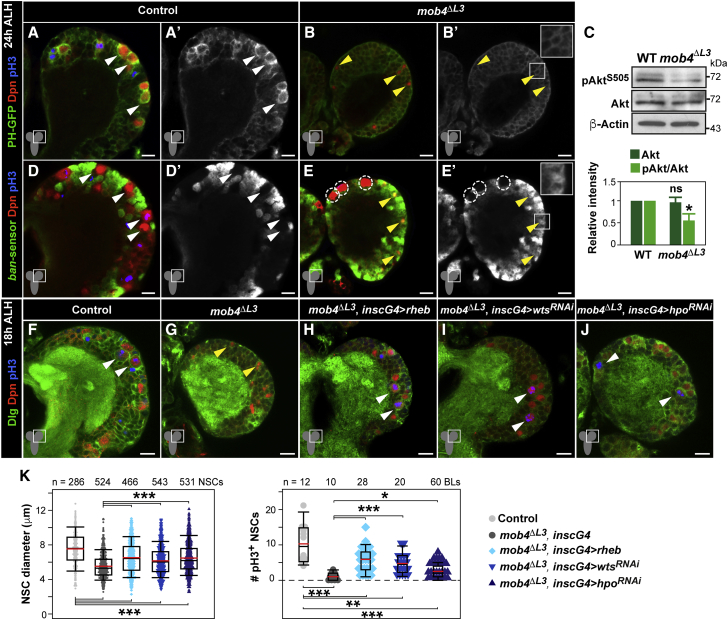
Figure 4.
InR/PI3K/Akt Pathway Activation or Hippo Signaling Inhibition Rescues NSC Reactivation in mob4 Mutants
(A–C) InR/PI3K/Akt signaling is strongly reduced in mob4 NSCs. Expression of pleckstrin homology (PH) domain-GFP fusion (GFP, green) does not accumulate at NSC membranes of mob4 mutants as in controls. Brain lobes of control (A) and mob4ΔL3 mutants (B) at 24 h ALH. NSCs in red (Dpn) and divisions in blue (pH3). GFP channel also shown in monochrome (A’ and B’). Inset displays higher magnification (B’). Yellow arrowheads: quiescent NSC examples; white arrowheads: reactivated NSC examples.
(C) Phospho-Akt (pAktS505) is reduced in mob4 mutant brains, while total Akt levels are comparable to those in controls (24 h ALH brain extracts; β-actin: loading control). Quantification of protein signals (bottom; error bars: SEMs; n = 3 independent assays; Student’s t tests; ∗p < 0.05; p > 0.05: ns.
(D–E’) Hippo signaling remains active in mob4 NSCs. In contrast to controls, NSCs in mob4 mutants show no ban activity, except in MbNSCs (dashed circles). ban-activity sensor, in which decreased GFP signal (green) reflects increased ban activity, in brain lobes of control (D and D’) and mob4ΔL3 mutants (E and E’) at 24 h ALH. NSCs in red (Dpn) and divisions in blue (pH3). GFP channel also shown in monochrome (D’ and E’). Inset showing higher magnification (E’).
(F–K) NSC-specific expression of rheb activating InR/PI3K/Akt signaling and of warts (wts)-RNAi or hippo (hpo)-RNAi inactivating Hippo signaling can rescue NSC reactivation in mob4 mutants. Brain lobes of control (F, insc-gal4), mob4ΔL3 (G), mob4ΔL3 expressing Rheb in NSCs (H, mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > rheb), mob4ΔL3 expressing wts-RNAi in NSCs (I, mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > wtsRNAi), and mob4ΔL3 expressing hpo-RNAi in NSCs (J, mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > hpoRNAi) at 18 h ALH. NSCs in red (Dpn), cell membranes in green (Dlg), and divisions in blue (pH3). Anterior up. Scale bars: 10 μm and 17 μm in insets.
(K) Quantification of NSC diameters (insc-gal4 n = 286 NSCs, 4 BLs, 3 brains; mob4ΔL3 n = 524 NSCs, 7 BLs, 7 brains; mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > rheb n = 466 NSCs, 6 BLs, 5 brains; mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > wtsRNAi n = 543 NSCs, 8 BLs, 5 brains; mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > hpoRNAi n = 531 NSCs, 8 BLs, 5 brains) and divisions (insc-gal4 n = 12 BLs, 12 brains; mob4ΔL3 n = 10 BLs, 10 brains; mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > rheb n = 28 BLs, 14 brains; mob4ΔL3; insc-gal4 > wtsRNAi n = 20 BLs, 10 brains; mob4ΔL3, insc-gal4 > hpoRNAi n = 60 BLs, 30 brains).
Wilcoxon rank-sum tests; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.