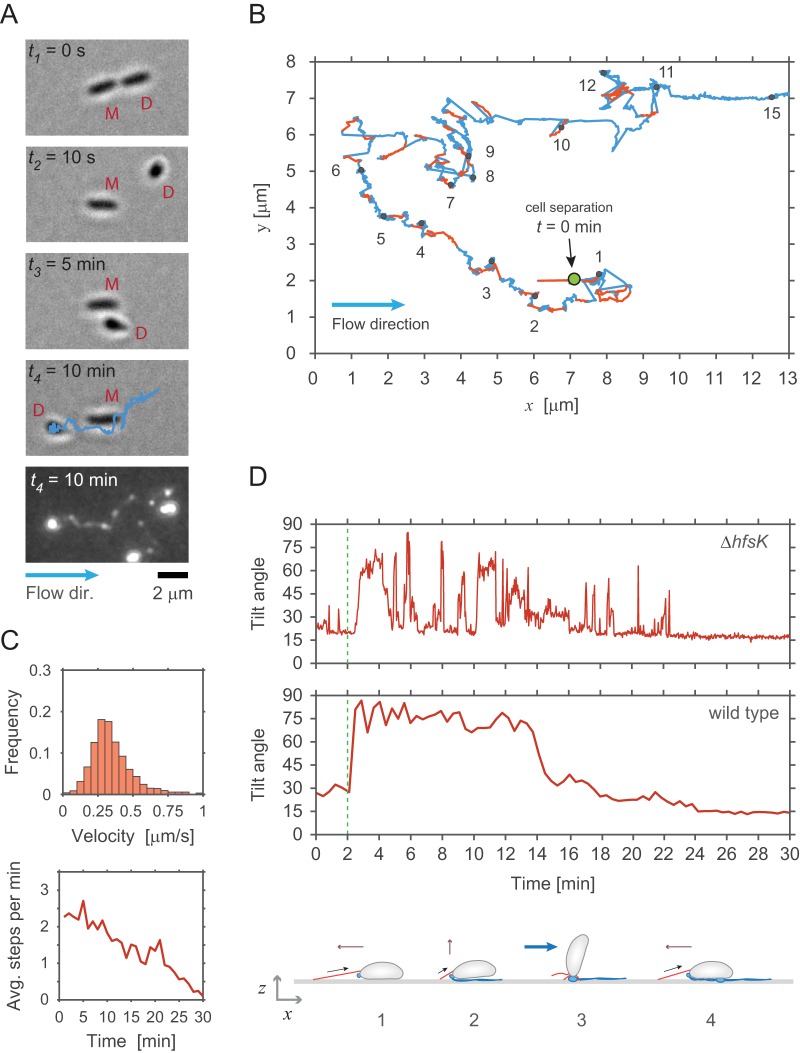
FIG 3.
Dynamic pili assist walking-like movements against the medium flow. (A) Example of a newborn SW cell of a ΔhfsK mutant moving against the medium flow. The secretion of holdfast adhesin is monitored microscopically by employing fluorescently labeled wheat germ agglutinin (bottom image). The time after cell division is indicated, and mother (M) and daughter (D) cells are individually labeled. Time points t1 and t2 show the SW cell immediately before and after separation from its mother. Time points t3 and t4 show how the SW cell moves against the medium flow (blue arrow) past its mother. The blue track, which indicates the trajectory of the cell recorded during its 10 min walk, perfectly matches trails of holdfast material left behind. (B) Representative trajectory (blue line) of a SW cell moving on the surface of a microfluidic channel. The trajectory is reconstructed from time-lapse images recorded for a single cell of the ΔhfsK mutant. Step events were identified as fast movements against the flow and are highlighted in red. Black dots in the track indicate the time (minutes) after cell separation. (C) Pilus-mediated walking speeds (upper chart) and average number of step events per minute (lower chart) recorded for SW cells of the ΔhfsK mutant at the time points indicated after cell division (time zero) (n = 56). (D) SW cells were repeatedly standing up during movements against medium flow. The tilt angle θ was recorded over time for representative examples of walking SW cells of a ΔhfsK mutant (upper panel) and the wild type (lower panel). A schematic of walking movements of the ΔhfsK mutant is shown below the charts. Retraction of an extended pilus pulls a horizontally positioned cell forward (step 1). Upon full retraction of the pilus, the cell body is pulled into an upright position (step 2), against the drag force of the medium flow (step 3). Upon completion of pilus retraction, the cell is pushed back onto the surface by flow (step 4) followed by the next motility step catalyzed by an extended pilus.