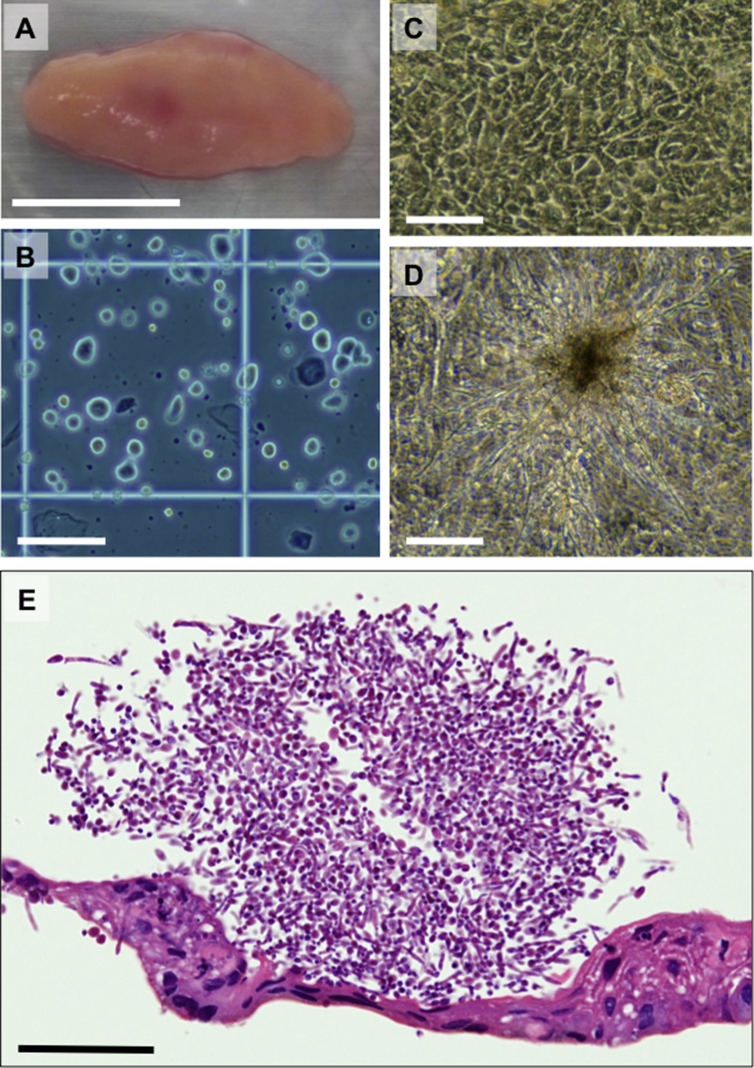
Fig. 1.
Candida albicans (C. albicans) proliferating in the cell culture supernatant of human oral mucosal epithelial cells in this clinical study. (A) Human oral mucosal tissue of the patient. Bar = approximately 1 cm. (B) Oral mucosal epithelial cells derived from the patient after cell preparation. Bar = 100 μm. (C) Cellular morphology of the cultured human oral mucosal epithelial cells. Bar = 100 μm. (D) C. albicans observed on the cultured epithelial cells in a culture vessel. Bar = 100 μm. (E) Histological observation of the C. albicans adhering to a cultured epithelial cell sheet harvested from a temperature-responsive culture insert. The cell sheet and C. albicans were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Bar = 50 μm.