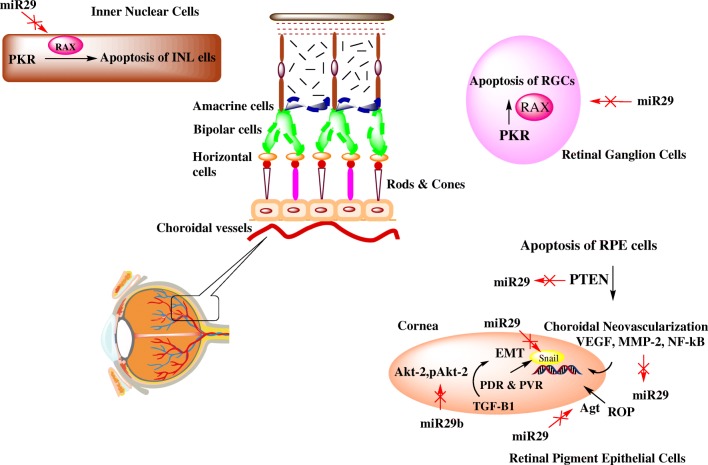
Fig. 1.
The schematic demonstrates the crosstalk between miR29 family and several signal transduction pathways involved in pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. In inner nuclear cells and retinal ganglion cells, miR29 shows its protective action via targeting PKR pathway and inhibition of RAX to prevent cells’ apoptosis while in retinal pigment epithelial cells, apoptosis is prevented via inhibition of PTEN pathway. Choroidal Neovascularisation occurs in RPE cells via suppression of miR29 and upregulation of VEGF, MMP-2 and NF-κβ. miR29 prevents ROP via targeting Ang II. In addition to this, miR29 targets transcription factor, Snail as well as Akt-2 and pAkt-2 involved in progression of EMT. However, TGF-β1 downregulates miR29 and promotes EMT. PKR, Protein kinase RNA-activated pathway; RAX, Retinal homeobox protein; PTEN, Phosphatase and tensin homolog; RPE, Retinal pigment epithelial cells; VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor; MMP-2, Matrix metalloproteinase-2; NF-κβ, Nuclear factor-κβ; ROP, Retinopathy of prematurity; Ang II, Angiotensin II; Akt-2 and pAKt-2, serine/threonine specific protein; EMT, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; TGF-β1, Transforming growth factor-β1