Fig. 1.
The endocannabinoid system.
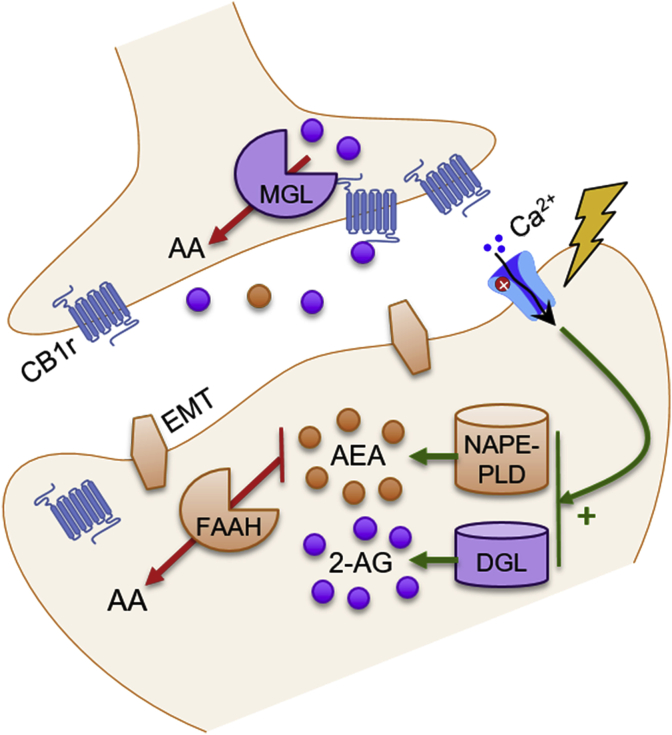
This schematic illustrates the basic components of the endocannbinoid (eCB) system. Postsynaptic depolarization and influx of calcium (Ca2+) stimulates eCB synthesis. N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-hydrolyzing phospholipase-D (NAPE-PLD) is the main enzyme responsible for synthesizing anandamide (AEA), while diacylglycerol lipase (DGL) synthesizes 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). These eCBs can then cross through the membrane, either via passive diffusion or with the help of endocannabinoid membrane transporters (EMTs), and travel across the synapse, where they retrogradely activate presynaptic cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1r). Presynaptic monoacylglycerol (MGL) then metabolizes 2-AG, and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) breaks down AEA into arachidonic acid (AA).