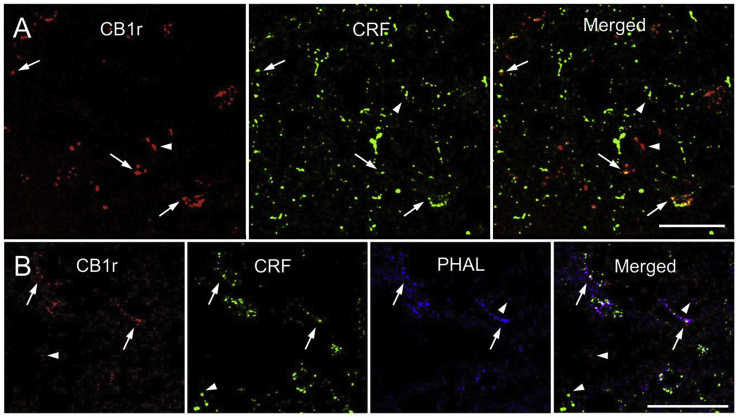
Fig. 3.
Co-localization of CB1r and CRF-amygdalar afferents in the LC. A.
Confocal fluorescence micrographs showing that cannabinoid type 1 receptor (CB1r, red) and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF, green) are co-localized in the locus coeruleus (LC). CB1r was detected using a rhodamine isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody and CRF was detected using an Alexafluor 647-conjugated secondary antibody (pseudocolored in green). Co-localization of CB1r and CRF (yellow) is shown in a merged image. Arrows highlight points of CB1r and CRF co-localization, while arrowheads point to singly labeled points of CB1r and CRF. B. Confocal fluorescence micrographs showing that CB1r (red), CRF (green), and phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin (PHAL, blue) are co-localized in the LC. CB1r was detected using a rhodamine isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody, CRF was detected using an Alexafluor 647-conjugated secondary antibody (pseudocolored in green), and PHAL was detected using fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody (pseudocolored in blue). Triple co-localization (white) can be observed, and is depicted by arrows. Arrowheads highlight singly labeled points of CB1r, CRF, and PHAL. This figure represents data previously published in (Wyrofsky et al., 2017). Scale bars = 25 μm. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)