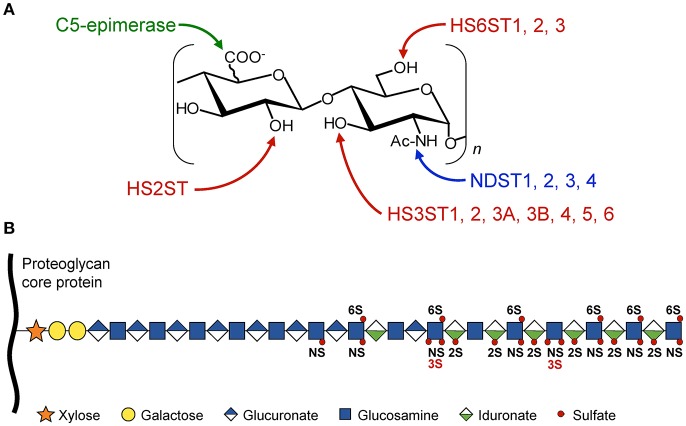
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of HS modifications. The HS polysaccharide is linked by the tetrasaccharide linker [Xyl-Gal-Gal-GlcUA] to a specific serine residue within the HSPG core protein. Elongation of the chain is achieved through the alternative addition of GlcUA and GlcNac residues by the polymerases EXT1/EXT2. (A) The disaccharide units [GlcUA-GlcNAc] are modified by the actions of sulfotransferases and epimerase. The sites of modification by N-deacetylases/N-sulfotransferases (NDST), C5-epimerase, HS 2-O-sulfotransferase (HS2ST), HS 6-O-sulfotransferases (HS6STs), and HS 3-O-sulfotransferases (HS3STs) are indicated. (B) HS modifications do not go to completion, resulting in domains with high, intermediate, and low levels of sulfation, enabling the generation of many HS structures and potential ligand-binding sites. NS, N-sulfo group on GlcN residue; 2S, 2-O-sulfo group on uronic acid residue; 3S and 6S, 3-O and 6-O-sulfo groups on GlcN residue.