FIGURE 1.
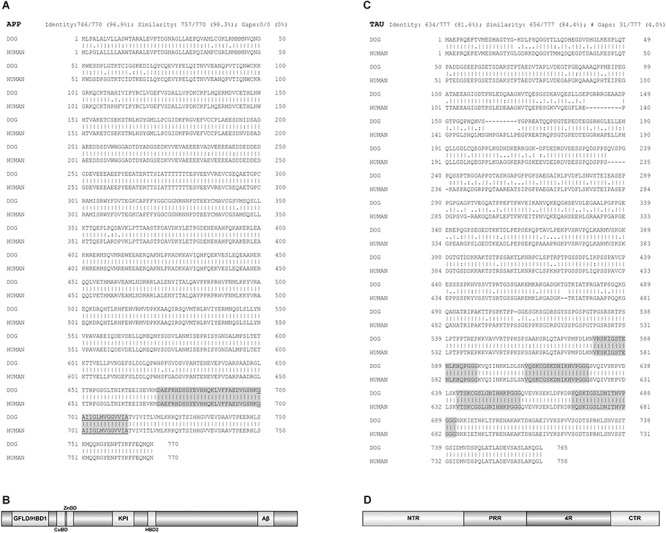
Protein sequences alignments between dog and human amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) and TAU. (A) The alignment of the longest canine APP isoform (APP-770) sequence with protein sequence of human APP. Aligned sequences share 96.9% amino acid identity and 98.3% similarity. Of note, the sequence identity of canine APP-695 isoform, the predominant APP isoform in the canine brain, and human APP is 87.5%. Highlighted is Aβ domain and underlined the membrane bound part of this domain. (B) Domain structure of APP. Isoform APP-770 is depicted. HBD1/GFLD, heparin binding domain 1/growth factor like domain; CuBD, copper binding domain; ZnBD, zinc binding domain; KPI, Kunitz-type protease inhibitor domain (not present in APP-695); Aβ, amyloid beta domain, the latter anchors APP in the cell membrane. The α-, β-, and γ-secretase cleavage sites are directly adjacent or inside the Aβ domain region, which is also most mutation prone, thus enabling alternative cleavage of APP and its divergent aggregation propensities. (C) Alignment of the longest TAU protein isoform, out of six existing, of dog and human TAU. Aligned TAU sequences share 81.6% amino acid identity and 84.4% similarity. Highlighted are four microtubule-binding regions (4R). (D) Domain structure of TAU. The basic organization is shown. NTR, N-terminal region; PRR, proline-rich region; 4R, four microtubule-binding regions (some isoforms have three); CTR, C-terminal region. The PRR and 4R domains are subject of most posttranslational modifications, while the CTR enables interactions with microtubules and plasma membrane. EMBOSS Needle pairwise sequence alignment (Madeira et al., 2019) was performed. A line (|) indicates positions which have a single, fully conserved residue. A colon (:) indicates conservation between groups of strongly similar properties and a dot (.) indicates conservation between groups of weakly similar properties. The domain organization was depicted by software illustrator of biological sequences (IBS) (Liu et al., 2015). Figure made by the authors.
