Figure 4.
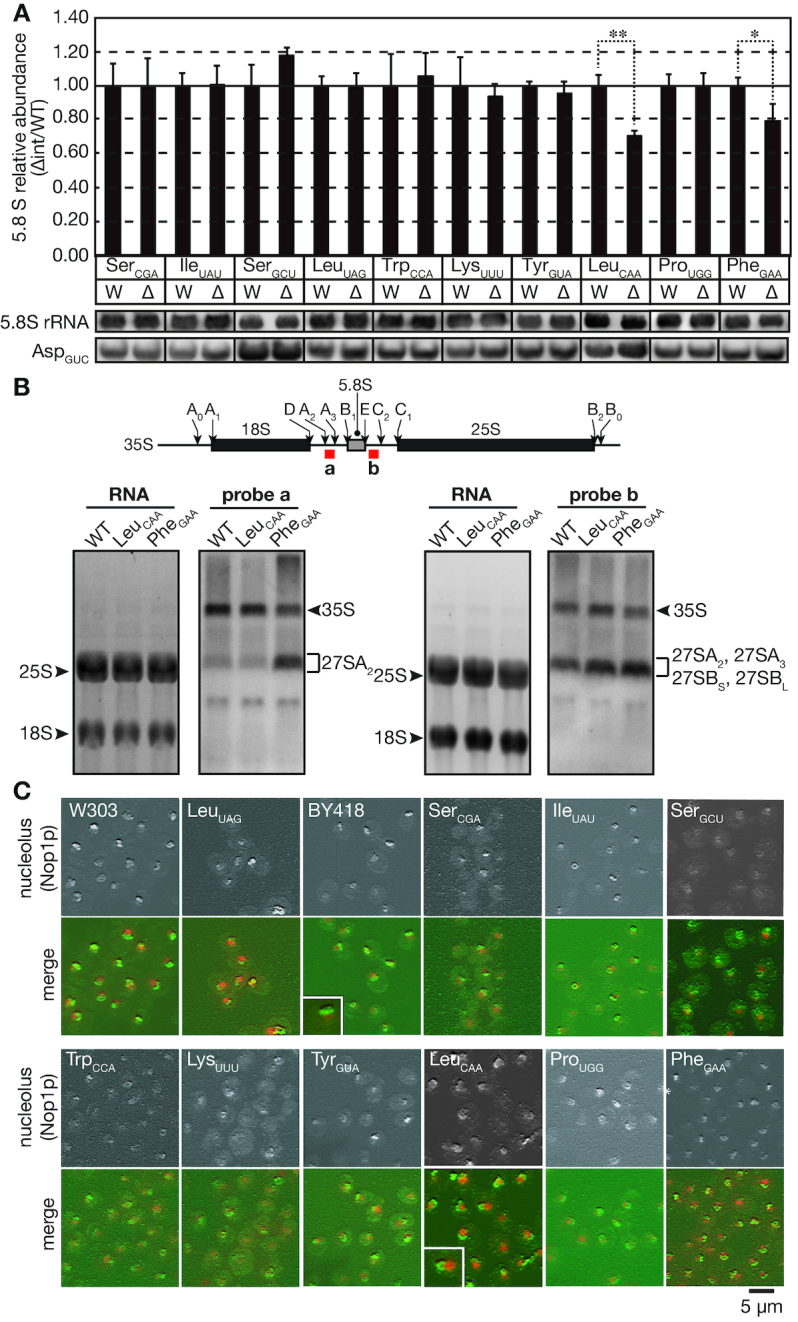
Intron removal from tRNALeuCAA genes reduces the 5.8S rRNA amount and alters nucleolar morphology. (A) Northern blotting analyses of 5.8S rRNA levels in the wild-type (W) and intronless (Δ) strains. Small RNA fractions were prepared, analyzed and quantified by northern blotting as described in Figure 3. Data represent the mean plus standard deviation (error bar) of three biological replicates. Because the RNA samples analyzed here were the same as those used in Figure 3, the same northern blotting data for tRNAAsp were used as an internal control. See the Figure 3 legend in detail. (B) Upper panel: Schematic illustration of the major processing sites of the 35S rRNA primary transcript. The hybridization regions of the probes are indicated by red boxes. Lower panel: RNAs from the wild-type (WT), tRNALeuCAA intronless and tRNAPhe intronless strains were analyzed by northern hybridization with probes against the A2-A3 region in ITS1 (probe a, second panel) and the E-C2 region in ITS2 (probe b, fourth panel) of the 35S rRNA precursor. Total RNA staining with SYBR Green II of the agarose gels is shown in the first and third panels. Assignment of intermediates was according to (37). (C) Immunofluorescence images of nucleolar morphology in the wild-type strains (W303-1A, BY418) and the indicated intronless strains. Yeast strains grown in YPD at 30°C were fixed and subjected to immunofluorescence with an anti-Nop1p (nucleolar marker) antibody, and DAPI was used to stain the nucleus. The upper panel in each set of images represents a 3D reconstruction image of the Nop1p stain, and the lower panel is the merged image of the Nop1p stain (green) and the DNA stain (red). The small boxed areas are enlarged images of the nucleolus in the wild-type and that of the typical nucleolus with an abnormal shape in the tRNALeuCAA intronless mutant.
