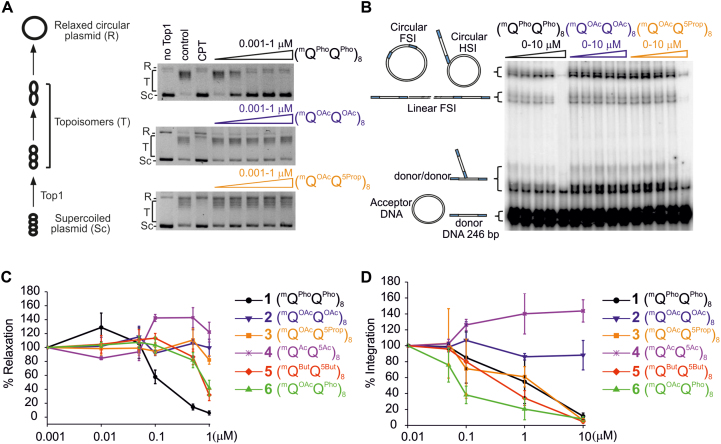
Figure 7.
Enzyme inhibition. (A, B) Representative gel electrophoresis of (A) the inhibition of Top1-mediated relaxation of supercoiled circular DNA and (B) in vitro HIV-1 IN integration (200 nM of IN) of a radio-labelled 246-base-pair (bp) viral DNA donor (10 nM) into a 2,700 bp pZeo plasmid acceptor (2.8 nM). In (A), lane 1 is DNA alone, control lane 2 is DNA + Top1 and lane 3 is the same as lane 2 in the presence of 50 μM camptothecin (CPT). The control lane 2 shows full Top1 activity. Camptothecin (CPT) is a classical Top1 inhibitor. In (B), for each foldamer, the left lane is the control lane (i.e. all things equal but without any foldamer). The position and structures of the donor substrate and different products obtained after half-site (HSI), full-site (FSI) and donor/donor integration are shown. (C, D) Quantitation of (C) Top1 inhibition expressed as a percentage of relaxation, compared to the control, and (D) in vitro HIV-1 IN integration. In (D), the circular FSI + HSI and linear FSI products were quantified on gels using the ImageJ software and the circular and linear HSI + FSI is reported as the percentage of heterointegration quantified in the absence of foldamers. Results are the means of at least triplicate experiments ± standard deviation.