Figure 3.
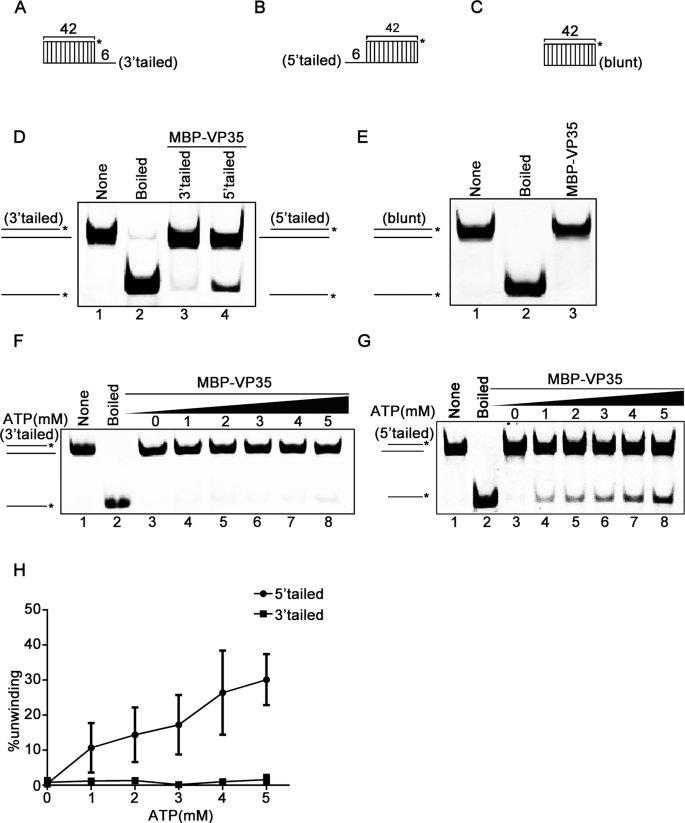
EBOV VP35 unwinds RNA helix in the 5′ to 3′ directionality. (A–C) Schematic illustrations of the RNA helix substrates with 3′-tailed (A), 5′-tailed (B), and blunt ends (C). Asterisks indicate the HEX-labeled strand. (D and E) MBP–VP35 (20 pmol) was reacted with 0.1 pmol 3′-tailed (lane 3) or 0.1 pmol 5′-tailed (lane 4) RNA helix substrate (D), or 0.1 pmol helix substrate with blunt ends (E). (F and G) MBP–VP35 (20 pmol) was reacted with 0.1 pmol 3′-tailed (F) or 5′-tailed (G) RNA helix substrate in the presence of increasing concentrations of ATP. (H) The unwinding activities were plotted as the percentage of the released RNA from the total 3′-tailed (F) or 5′-tailed (G) RNA helix substrate (Y-axis) at each ATP concentration (X-axis). The error bars represent SD values from three separate experiments.