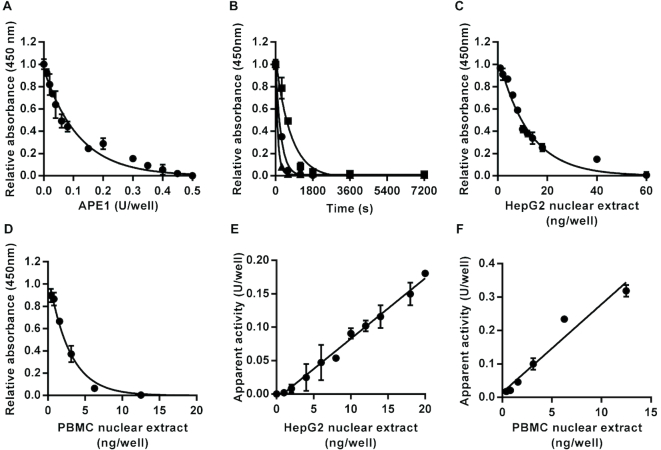
Figure 2.
Effect of apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site incision activity on an oligonucleotide substrate containing a single tetrahydrofuran AP site analog. Incubation with recombinant human APE1 led to enzyme concentration-dependent (A) and time-dependent (B) decreases in the amount of intact substrate retained in the wells after neutral denaturation. For the time course analysis squares, circles and triangles indicate data generated with 0.1, 0.2 or 0.4 units/well, respectively. Incubation with HepG2 nuclear extract (C) or PBMC pooled nuclear extract (D) also caused concentration-dependent decreases in the amount of intact substrate retained in the wells. The apparent AP site incision activity was directly proportional to the concentration of nuclear extract over the range 0–0.02 μg/well for the HepG2 nuclear extract (r2 = 0.99) (E) and over the range 0–0.0125 μg/well for the peripheral blood mononuclear cell nuclear extract (r2 = 0.95) (F). Data shown represent the mean ± SD of triplicate technical replicates except for time course data for which duplicates were analyzed.