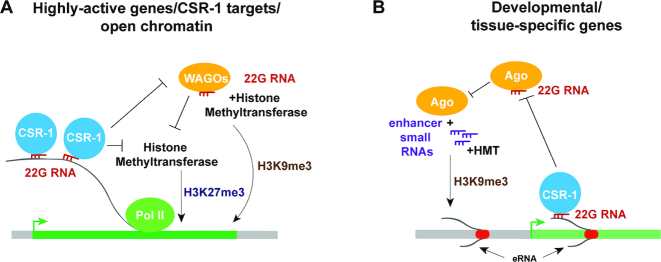
Figure 6.
Models describing connections between small RNAs and chromatin at actively transcribed genes (A) and at enhancer regions (B). RdRP complexes that include the DRH-3 helicase (not shown) produce 22G-RNAs (red), which are loaded onto CSR-1 or WAGO Argonautes. Enhancer small RNAs (purple) are generated in RdRP-independent manner. (A) 22G-RNAs in complex with CSR-1 Argonaute bind nascent transcripts of highly active genes, thus protecting the latter from WAGO-bound 22G-RNAs that guide H3K9me3, which is associated with silencing. Either active transcription facilitated by CSR-1 Argonaute or silencing by WAGO (when CSR-1 is deficient) prevent H3K27me3-modulated silencing through additional mechanisms. (B) CSR-1-associated 22G-RNAs bind some enhancer-derived transcripts, protecting them from silencing by other mechanisms. When CSR-1 or RdRP-produced 22G-RNAs are limited, other Argonautes may load enhancer small RNAs that accumulate in these regions. This may lead to silencing through H3K9 methylation driven by Argonaute proteins and associated methyltransferases.