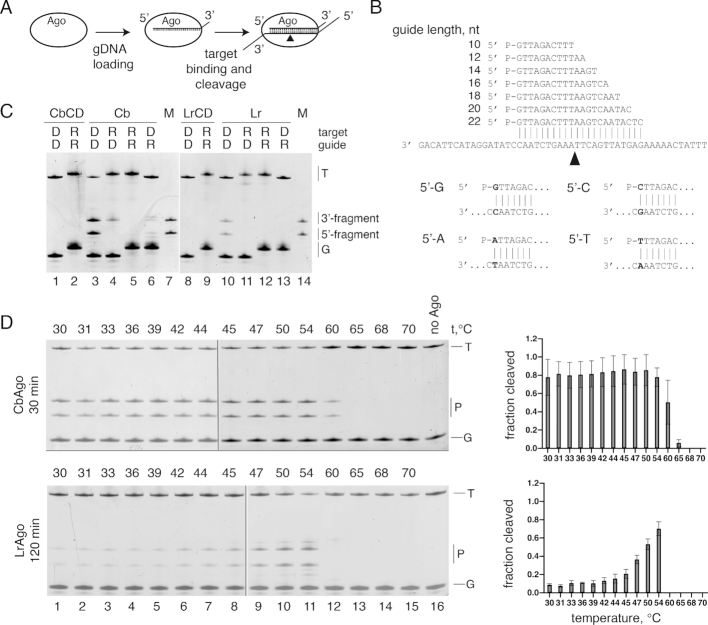
Figure 1.
CbAgo and LrAgo are DNA-dependent DNA-endonucleases. (A) Scheme of the in vitro assay. (B) Guide and target oligonucleotides. DNA guides and targets were used in most experiments; 18 nt guide and 50 nt target RNAs were additionally used for analysis of pAgo specificity (see panel C). Black triangle indicates the predicted cleavage site between target positions 10′ and 11′ (corresponding to the guide positions 10 and 11 starting from the 5′-end). Four guide-target pairs with different nucleotides in the guide 5′-end are shown at the bottom. (C) Analysis of the cleavage specificity of pAgos. Wild-type (WT) or catalytically dead (CD) CbAgo and LrAgo were loaded with 18 nt DNA (D) or RNA (R) guides and incubated with 50 nt ssDNA or RNA targets for 2 hours at 37°C. Positions of the guides (G), targets (T) and cleavage products (P) are indicated on the right of the gels. The marker (M) lane contains synthetic oligonucleotides corresponding to the expected cleavage products (23 nt 5′-end and 27 nt 3′-end target fragments). (D) Temperature dependence of ssDNA cleavage by CbAgo and LrAgo. The assay was performed for 30 min (CbAgo) or 2 h (LrAgo) at indicated temperatures. Quantification of the cleavage efficiencies (the percentage of target cleavage) is shown on the right.