Figure 1.
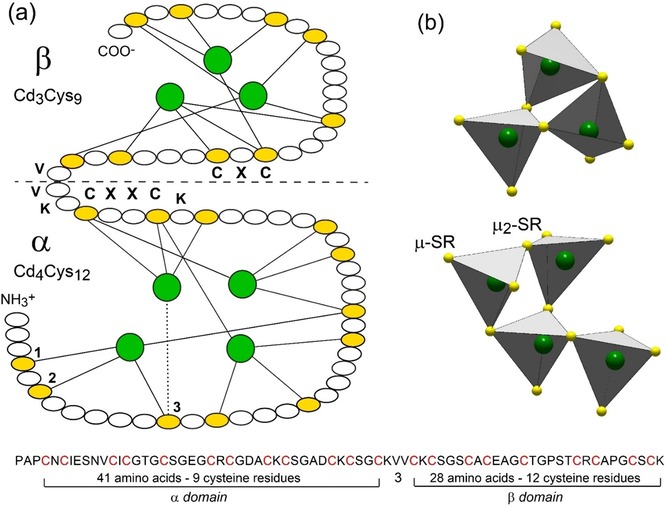
Primary structure of Cd7‐MT from mussel MT‐10 and Cd‐thiolate connectivity in the two clusters. (a) Amino acid sequence of the α‐ and β‐domains,14a showing the 21 Cys residues (in yellow) and Cd3Cys9 and Cd4Cys12 clusters3b (in green). Cysteine represents 21/72=29 % of the total amino acids. The Cys residues are arranged in nine CXC, one CXXC, and five CXXXC motifs, where X can be any amino acid. The solid lines denote the CdII‐Cys bonds, and the dotted line indicates an ambiguous assignment between the Cys residues 1, 2, and 3 (only the last possibility is represented for clarity). The horizontal dashed line denotes the boundary between the two domains connected by a flexible linker segment of three amino acids (KVV). (b) Polyhedral representation of the connectivity of the Cd(Cys)4 tetrahedra in each domain. The Cd3Cys9‐β cluster has three bridging (μ2‐SR) and six terminal (μ‐SR) cysteinyl sulfur atoms, and the Cd4Cys12‐α cluster has four μ2‐SR and eight μ‐SR.
