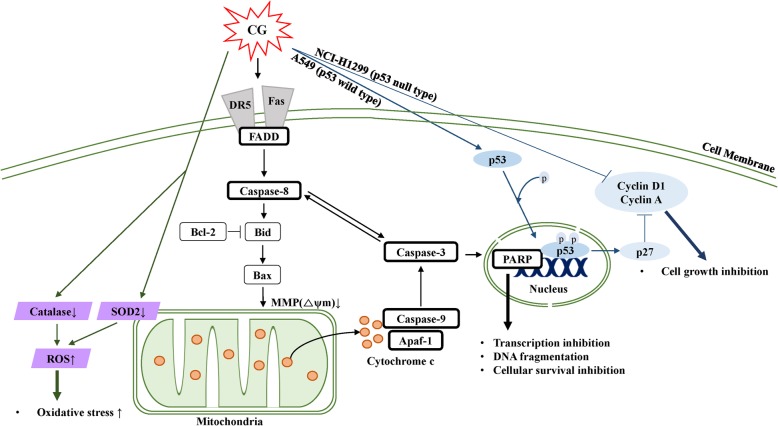
Fig. 9.
Schematic diagram illustrating CG-induced apoptotic effects in A549 and NCI-H1299 NSCLC cell lines. CG stimulated death receptor (DR5 and Fas)- and adaptor (FADD)-mediated apoptotic signaling pathways, as well as caspase-8 processing, which resulted in cytochrome c release that was regulated by Bcl-2, Bid, and Bax. Subsequently, caspase-9 and caspase-3 were activated, followed by cleaved PARP, which led to apoptosis. Furthermore, CG stimulated tumor suppressor p53, and the cell cycle was suppressed by a reduction in cyclin factors. Moreover, CG induced ROS generation through the control of ROS scavengers, such as SOD2 in mitochondria, and catalase