Figure 1. CM4620 blocks store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) in pancreatic acinar cells.
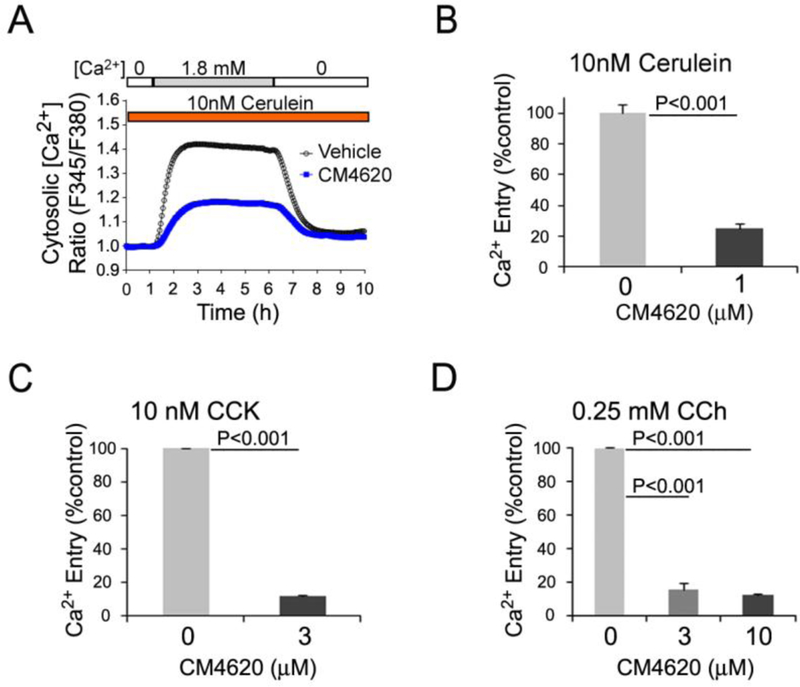
(A and B) Calcium levels in fura-2 loaded mouse pancreatic acini were monitored by fluorescence imaging microscopy. Acini were pretreated for 30 min with or without CM4620 at the indicated concentrations and then treated with Ca2+ mobilizing agents to induce Ca2+ release from ER stores. A, CM4620-induced blockade of SOCE in mouse acini stimulated with cerulein. Graph illustrates a representative trace showing the absence and presence of SOCE by fura-2 ratio (proportional to [Ca2+]c) in conditions of 0 mM (0 Ca) or 1.8 mM (1.8 Ca) Ca2+ in the extracellular media, respectively. CM4620 attenuated SOCE, indicating that Orai/STIM1 channels mediate SOCE in mouse acini. (B) Data obtained from multiple experiments similar to that shown in A show that cerulein-induced SOCE was approximately 80% blocked in fura-2 loaded mouse pancreatic acini by CM4620. (C) Fura-2-loaded mouse pancreatic acini were pretreated with or without CM4620 and then treated with cholecystokinin (CCK) as indicated in A. (D) Fura-2-loaded mouse pancreatic acini were pretreated with CM4620 and then treated with carbachol (CCh) as indicated in A. Levels of store-operated Ca2+ entry were quantitatively analyzed by comparing the areas under traces recorded in the presence or absence of CM4620 and with 1.8 mM Ca2+ in the extracellular media. Graphs show mean ±SD; n=3 independent cell preparations.
