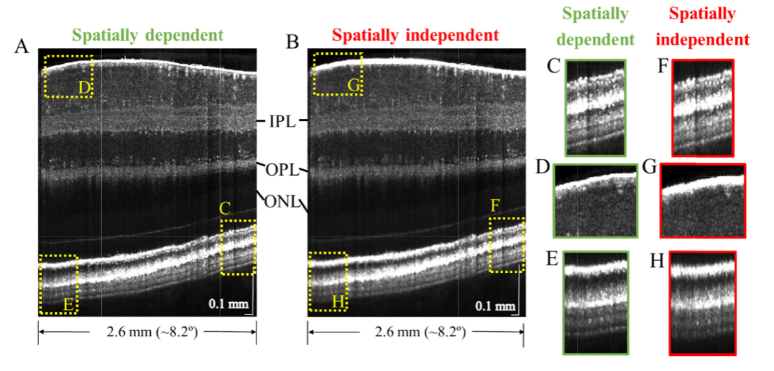
Fig. 5.
Visible light OCT image with spatially dependent (A) and spatially independent (B) dispersion compensation. While the spatially independent method can perform comparably to the spatially dependent method at a particular image location (C,F), the spatially dependent method optimizes image sharpness at all locations (D,E), whereas the spatially independent method does not (G,H), enabling more consistent and clear visualization of lamination across the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and outer plexiform layer (OPL). A depth-dependent grayscale, transitioning in the outer nuclear layer (ONL), simultaneously highlights relevant contrast in both the inner and outer retina.