Figure 1.
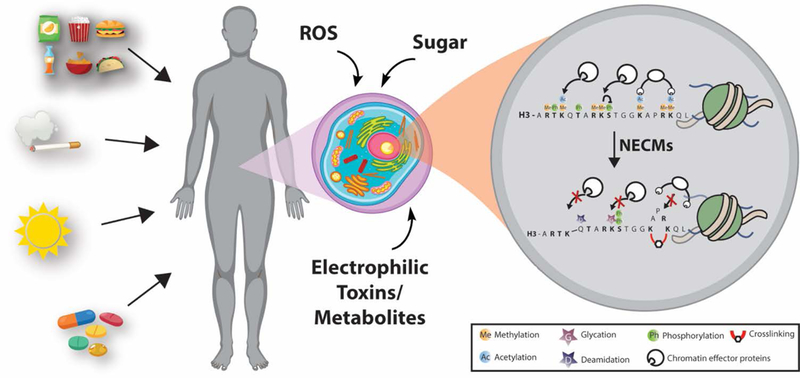
General schematic of NECM exposure and effect on chromatin. Environmental exposure to reactive metabolites through nutrition, toxins (automobile gas, pollution, cigarette smoke), damaging radiation (UV, ionizing), or drugs changes the cellular microenvironment and introduces highly reactive species. These toxins react with various proteins in the cell, but accumulate on histones, which have a very long half-life and highly accessible nucleophilic tails. Non-enzymatic modification of histones competes with other regulatory enzymatic modifications and changes chromatin architecture.
