Figure 5.
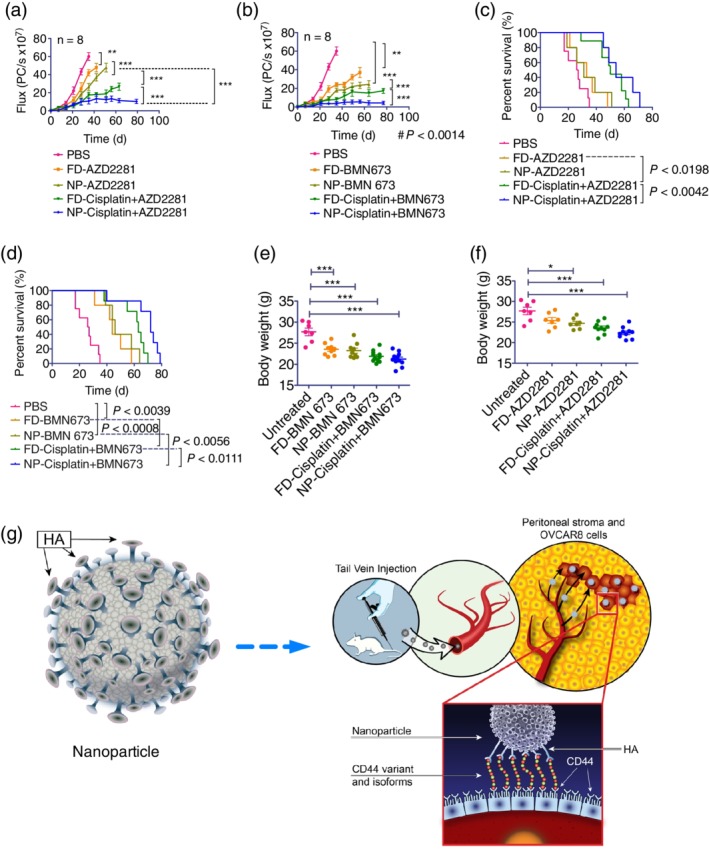
HA terminal‐layered polymeric liposomal nanoparticles produce a superior in vivo therapeutic response in HGSOC xenografts. NCR nude female mice bearing luciferase‐ and CD44‐expressing OVCAR8 xenografts were treated weekly via IV administration of vehicle, AZD2281, BMN 673, or cisplatin monotherapies or cisplatin combined with AZD2281 or BMN 673 (n = 8). (a and b) Plots of the bioluminescent signal flux of the tumors from the start of treatment. Statistical significance was determined by one‐way ANOVA with Turkey's multiple comparison tests. (c and d) Kaplan–Meier plots of survival fractions. Statistical significance was determined using the log‐rank (Mantel–Cox) test. (e and f) The body weight distribution of the treatment groups was measured and graphed as scatter plots. Statistical significance was determined by one‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison tests. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001. (g) Schematic illustration of the design of the polymeric liposomal nanoparticle assembly with loaded therapeutic cargo and the treatment mechanism. FD, denote free and NP‐encapsulated nanoparticles. HGSOC, high‐grade serous ovarian cancer; IV, intravenous
