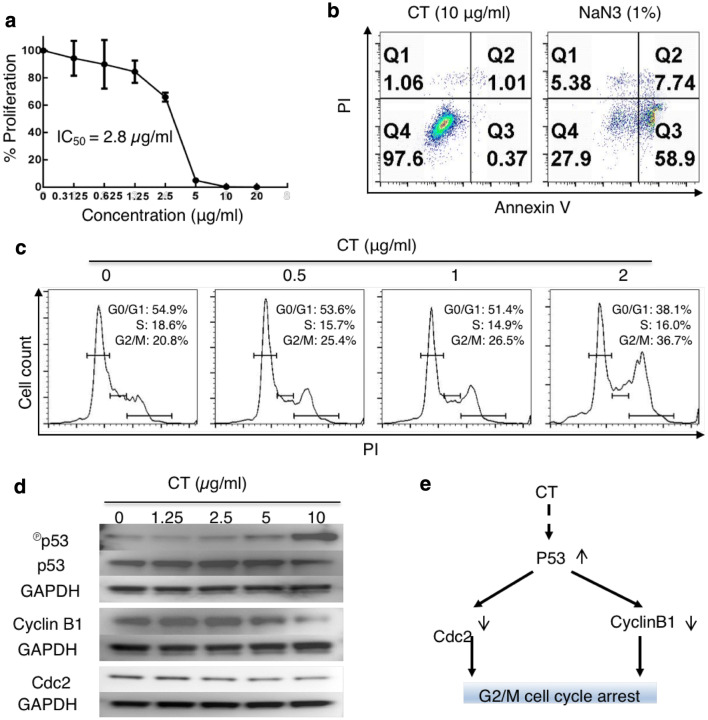
Fig. 1.
CT inhibited the proliferation of LLC through G2/M arrest with compatible intracellular signaling events. a LLC cancer cells were treated in triplicate in a 96-well plate for 48 h in a CO2 incubator with CT at indicated concentrations and their proliferation assessed by 3H-TdR incorporation. The % proliferation was calculated as (CPM with compound − CPM blank)/(CPM without compound − CPM blank) × 100. b LLC cells seeded in a 12-well plate at 3 × 105/ml/well were treated with various concentrations of CT or 1% NaN3 (as a positive control) for 24 h in a CO2 incubator. Subsequently, the cells were harvested and stained with an apoptosis detection kit. Only the dot plot (PI vs annexin V) of cells treated with 10 µg/ml of CT and 1% NaN3 is shown. c Synchronized LLC treated with various concentrations of CT for 48 h in a CO2 incubator was stained with PI and subsequently analyzed for cell cycle. The data were graphed using FlowJo. d LLC cells serum-starved for 24 h were treated with indicated concentrations of CT before lysis in 1 × SDS sample buffer at 107/ml. The samples were separated on a 4–12% gradient NuPAGE™ gel, transferred on a piece of Immobilon™ membrane, blocked, and reacted with anti-phospho-p53, anti-cyclin B1, or anti-Cdc2. The membrane used for probing phosphor-p53 was stripped and re-probed with anti-p53. After the images were taken, the membranes were stripped and re-probed with anti-GAPDH. e A chart illustrating CT-induced signaling pathways responsible for CT-induced G2/M arrest in LLC cells